
[ad_1]
Intel’s 14th-gen cell processor, code-named Meteor Lake, represents a dramatic shift from the chips Intel has shipped for years — and Intel has offered us with a ton of knowledge. If you don’t have time to wade by all of it, nonetheless, we’ve summed up a very powerful factors right here.
Here’s what it’s essential learn about Meteor Lake. For a way more detailed examination of what this new era of processors affords, please see our deep-dive into Meteor Lake.
Intel will model Meteor Lake because the Core Ultra, and it’ll launch on Dec. 14, Intel chief government Pat Gelsinger mentioned at its Intel Innovation convention.
1.) Big energy for half the facility
Intel historically has developed its processors alongside a “tick-tock” mannequin, the place an older chip was first migrated (“tick”) onto a brand new course of know-how, after which redesigned and sped up (“tock”). Michelle Johnston Holthaus, government vp and basic supervisor of the Client Computing Group at Intel, was blunt: with Meteor Lake, Intel is concentrating on the efficiency of its Thirteenth-gen mobile Raptor Lake chips, however at half the facility (whoa). Any efficiency increase might be left to the graphics block, the place Intel is anticipating double the efficiency of the Raptor Lake built-in GPU with its new XeLPG built-in graphics core.
It reminds us of Qualcomm’s older messaging with its Snapdragon PC processors, really: comparable efficiency as an older Core chip, an enormous graphics increase, and always-on connectivity. Intel is definitely providing each WiFi 7 and WiFi 6E in Meteor Lake, however with out the large advertising push Qualcomm has made.
2.) Intel builds Meteor Lake drastically completely different than previous CPUs
Traditional Intel “microprocessors” included each a CPU and a supplementary chip referred to as a PCH inside the identical package deal. Now, Intel is transferring to 4 chiplets or “tiles”: a CPU, “SOC,” graphics, and an I/O tile all throughout the general Meteor Lake package deal. Intel calls this a “disaggregated” strategy, permitting it to plan every tile by itself growth roadmap and enhance the general yields.
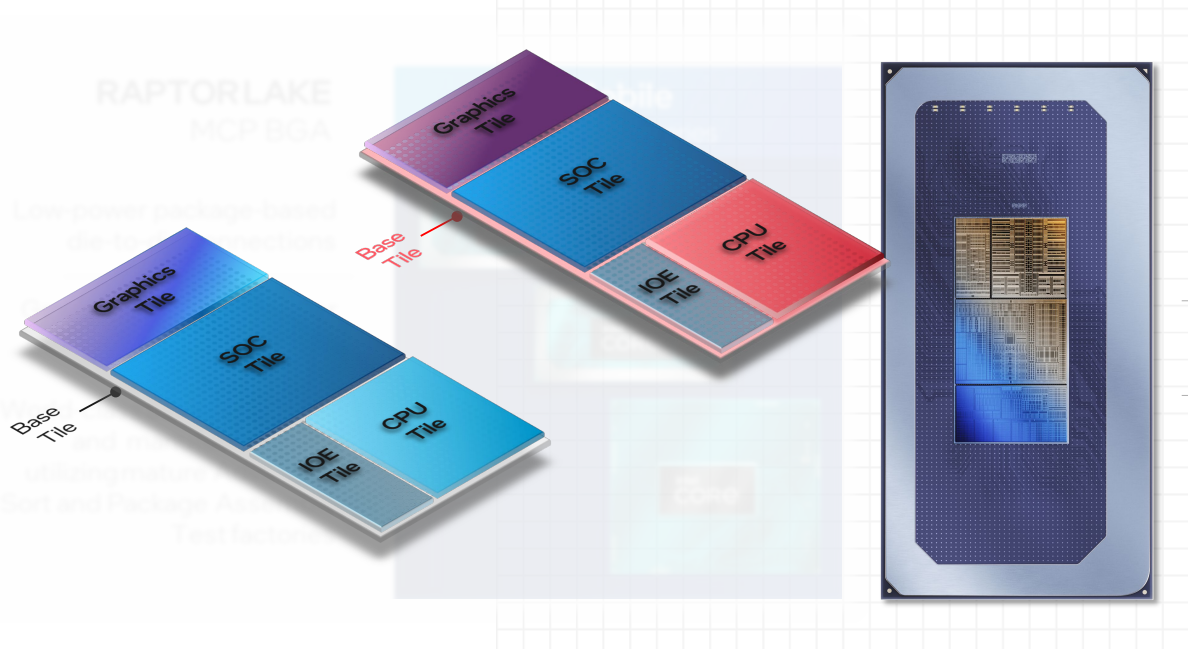
Intel
But the graphics and SOC tiles are made by rival TSMC. Only the CPU and (possibly) the I/O tile are made by Intel, with the CPU tile particularly made on Intel’s Intel 4 process. Intel, feeling the sting of years caught on a 14nm node, has dedicated to quickly stepping by 5 course of applied sciences in 4 years.
3.) Meet Meteor Lake’s new low-power E-cores
With the 12th-gen Alder Lake, Intel moved from one sort of processor core to 2: beefy efficiency cores (P-cores) and smaller effectivity cores (E-cores) for background duties. Now there’s a 3rd sort of processor core. In addition to the brand new “Redwood Cove” P-core and the brand new “Crestmont” E-core, there’s a low-power model of the Crestmont E-cores that might be used as the primary touchdown spot for duties which can be assigned to the CPU.
Intel isn’t saying how a lot sooner the P-cores are in comparison with these present in Raptor Lake. The Crestmont E-cores are between 4 to six p.c sooner, clock per clock. But right here’s one thing: Intel performed again a 4K video utilizing simply the low-power E-cores alone within the picture on the high of this story. That’s going to make a enormous distinction in your laptop computer’s battery life.
4.) No, critically, Meteor Lake is optimized for low energy
We’re not kidding. Intel’s Thread Director, the “butler” of the processor, takes duties that the working system assigns and routes them to the suitable cores. You could concentrate on how Thread Director worked in Raptor Lake: it could take duties or threads and push them to any efficiency cores (P-cores) that have been free. Raptor Lake pushed efficiency. In Meteor Lake, it’s precisely the alternative.
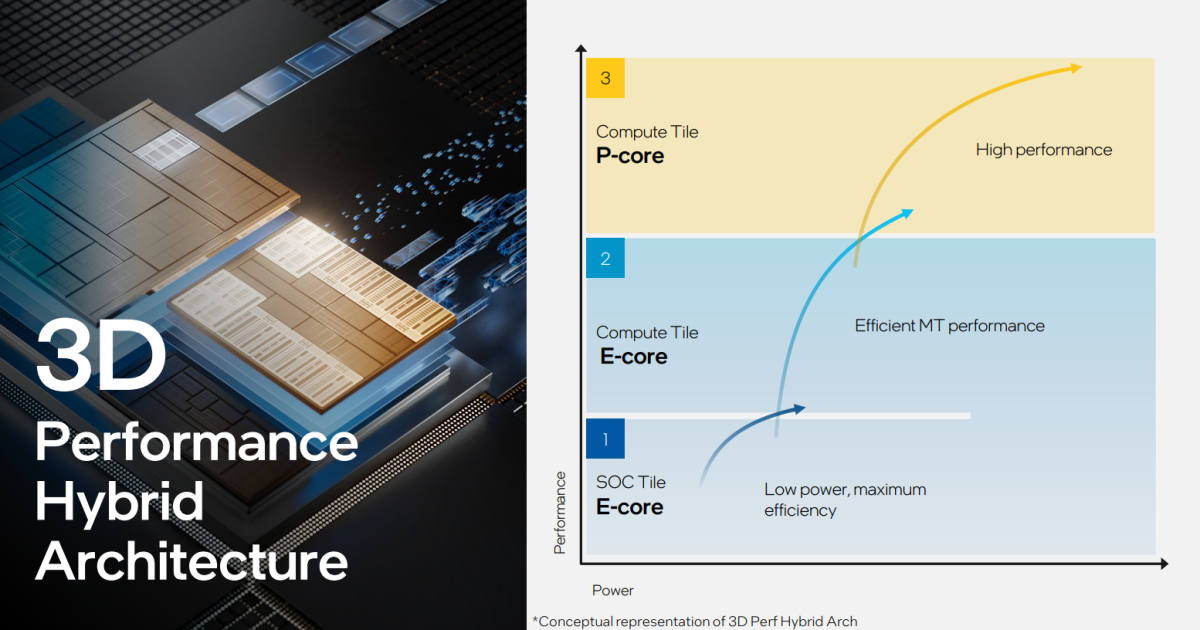
Intel
In Meteor Lake, new threads are routed to the low-power E-cores first, then the standard E-cores, after which to the P-cores themselves. It’s a coverage change, and it’s an enormous one. Even in a “performance” situation, new threads might be routed to the standard E-cores first, then the P-cores. Will it have an effect on the general efficiency of the chip? We don’t know.
5.) Welcome to the AI PC
The SOC tile is the place Intel’s NPU resides because the literal AI “brains” of the Meteor Lake chip. Intel’s NPU jogs my memory of the early days of GPUs: considerably primary, as each Intel, its clients, and builders determine what precisely AI is sweet for. (Remember, that is native AI — Bing Chat, Google Bard and different AI engines reside within the cloud. Why even have native AI in your PC? Privacy and pace, Intel says.)
The NPU, although, goes to energy what Intel calls the “AI PC.” Expect to listen to much more about that this week at Intel’s Innovation convention.
In AI, Intel’s actually simply making an attempt to speed up what it will probably: Windows capabilities, plus APIs just like the OpenVINO API that some builders use. Intel outlined what’s contained in the NPU at Innovation, however it received’t make a lot sense — but — even for many fans who’re intimately acquainted with threads, cores, TDPs, cache hierarchies and the like. Over time, we’d count on Intel will determine what clients want and speed up it.
Mark Hachman / IDG
One fascinating level: accelerating AI with an NPU would be the most effective by way of energy consumption. But by way of uncooked pace, a mixture of CPU, GPU, and NPU makes essentially the most sense, Intel says.
6.) Meteor Lake’s graphics present a ray-tracing increase
According to Intel, Meteor Lake takes one of the best components of the XeHPG graphics know-how discovered inside Intel’s Arc graphics cards and places it inside Meteor Lake’s GPU. That means, in brief, a doubling of the built-in graphics efficiency from Raptor Lake to Meteor Lake, in addition to built-in ray tracing assist.
While Intel isn’t releasing benchmarks but (and we don’t have the chip accessible for testing), Intel shared a few of its “micros,” or inner benchmarks: triangle draw fee improves 2.6X over Raptor Lake, with pixel mix charges bettering by 2.1X. While evaluating the depth check fee, nonetheless, Intel noticed a 6.6X enchancment.
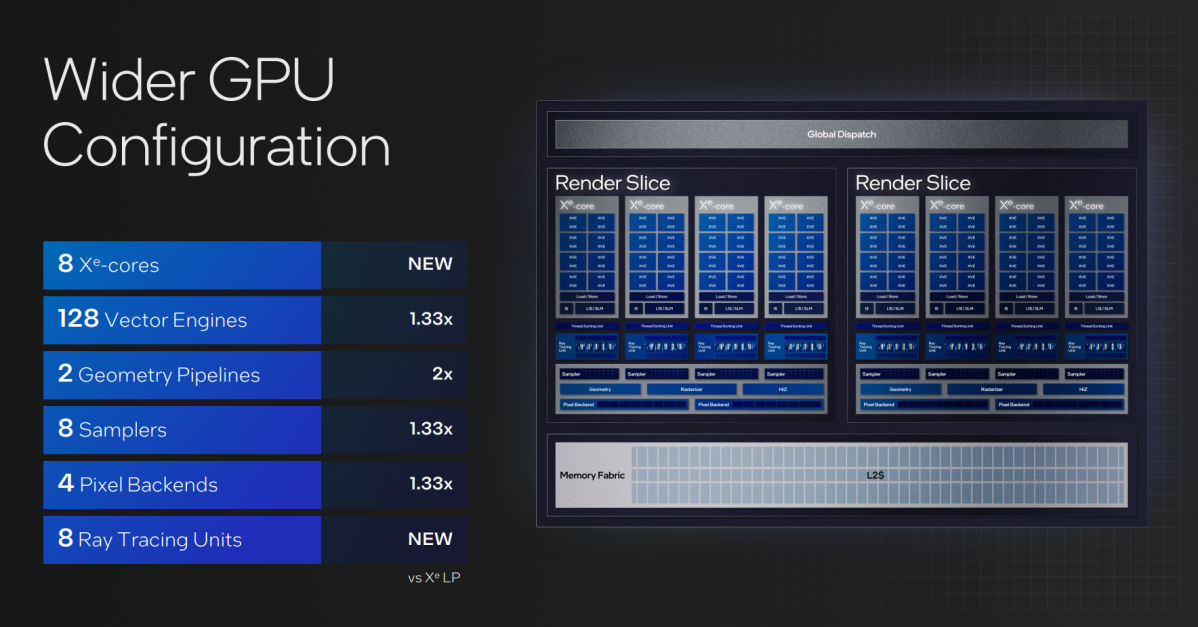
Intel
The Meteor Lake GPU additionally helps XeSS, Intel’s reply to the AI-powered DLSS know-how that upsamples a lower-resolution picture to enhance picture processing. And there’s one thing new by way of low-power (there’s that phrase once more!) gaming, too: Endurance Gaming, which is able to permit players on the go to increase their laptop computer’s battery life dramatically. According to Intel execs, the Meteor Lake GPU can render Rocket League at lower than 1W of energy.
What are Meteor Lake’s specs?
They’re not right here but, at the very least formally. Intel sometimes explains how its processors work first, then affords all of the essential shopping for info you’ll want, later. Unfortunately, you’ll have to attend till nearer to the official launch (sometimes on the CES present in Las Vegas in January) for the official speeds and feeds.
We do know that Intel confirmed off a six P-core, eight E-core implementation of Meteor Lake in Malaysia. Unfortunately, Intel is saying solely that it was for “demonstration purposes” and extra info might be shared nearer to launch.
In the meantime, we’ll watch for AMD’s Ryzen 8000 sequence chips to roll out subsequent 12 months, and information of Qualcomm’s Oryon sequence (based mostly upon its Nuvia processor know-how) to hopefully be disclosed in October.
(Disclosure: whereas we anticipated Intel to launch Meteor Lake at its Intel Innovation convention, it as a substitute flew journalists and analysts to its meeting and check services in Penang, Malaysia. Intel paid for PCWorld to attend, together with airfare, lodge and meals. To achieve entry to this info, PCWorld accepted, although it maintained editorial independence all through and doesn’t have an effect on our Meteor Lake protection. This story was up to date at 9:29 AM on Sept. 19 with extra particulars.)
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link