
[ad_1]
Intel’s new 14th-gen Core chip, Meteor Lake, is designed as a lot for Intel as it’s for you. A brand new disaggregation scheme separates the “processor” into 4 tiles, reducing energy and rising yields. But a doubling of graphics efficiency and a brand new AI engine helps cater to customers searching for new options.
Let’s be clear, although: Meteor Lake was not designed with CPU efficiency in thoughts. Intel executives describe Meteor Lake as providing the efficiency of the present Thirteenth-gen chip, Raptor Lake, however at half the ability — aided by new low-voltage effectivity cores (E-cores) which are new to the platform. Even the way in which Intel assigns CPU duties has been flipped on its head, pushing them first in the direction of the lowest-power E-cores, then migrating them to the extra power-hungry efficiency cores if want be.
Intel unveiled its new Meteor Lake platform in an offsite press occasion in Penang, Malaysia, although the corporate will speak extra about Meteor Lake at its Intel Innovation convention in San Jose this week.
At Intel’s Intel Innovation convention in San Jose, Intel chief government Pat Gelsinger added two extra particulars: that Meteor Lake will launch on Dec. 14, and it is going to be branded because the Core Ultra. Acer appeared on stage to indicate off its personal Meteor Lake laptop computer, and Intel used MSI-branded laptops in Malaysia.
Intel sometimes unveils a brand new chip in two elements: a basic architectural overview, explaining the way it all works; after which the data that helps affect shopping for selections, such because the mannequin numbers, speeds, costs (the place relevant), and so forth. Intel’s solely explaining what’s inside its new Core chip, for now. The chip maker isn’t saying when it’s going to ship Meteor Lake, however our guess is that the primary chips will exit the door this fall, with January’s 2024 CES present in Las Vegas serving as a venue to launch the chip into mainstream notebooks.
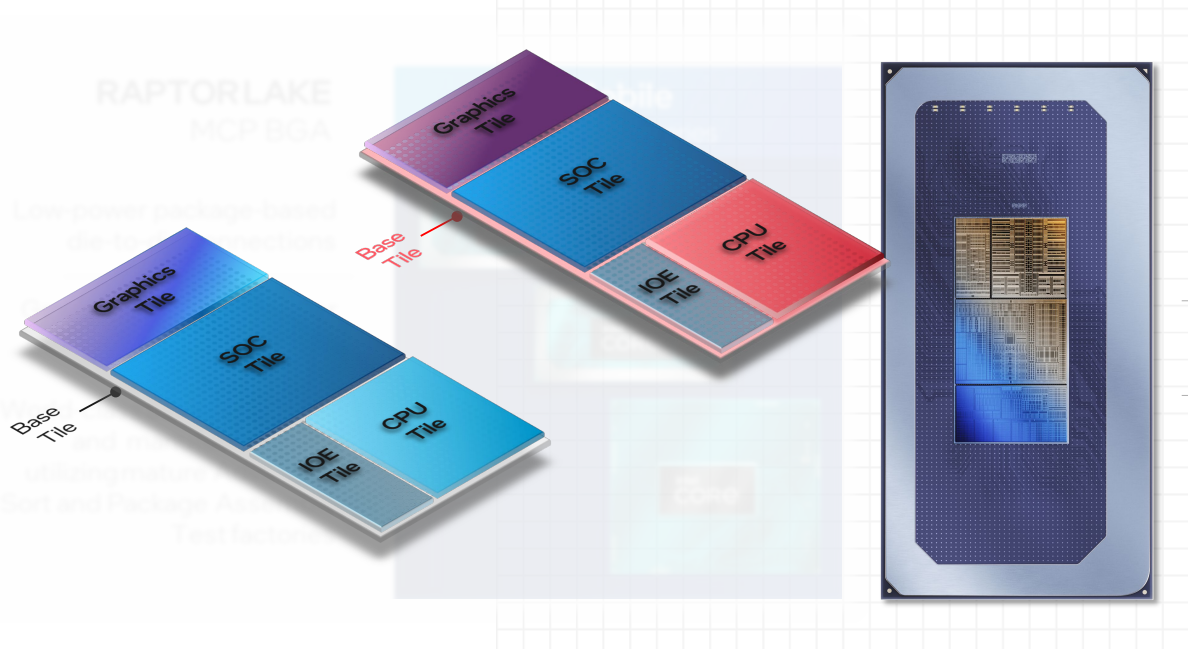
As you may count on, Intel’s new Meteor Lake is kind of difficult. Breaking it down into its element elements, nonetheless, appears to take advantage of sense. Intel’s Meteor Lake has 4 tiles: one every for the CPU, the SOC, graphics, and I/O. We’ll clarify every in flip, digressing the place essential to elucidate how Meteor Lake all suits collectively.
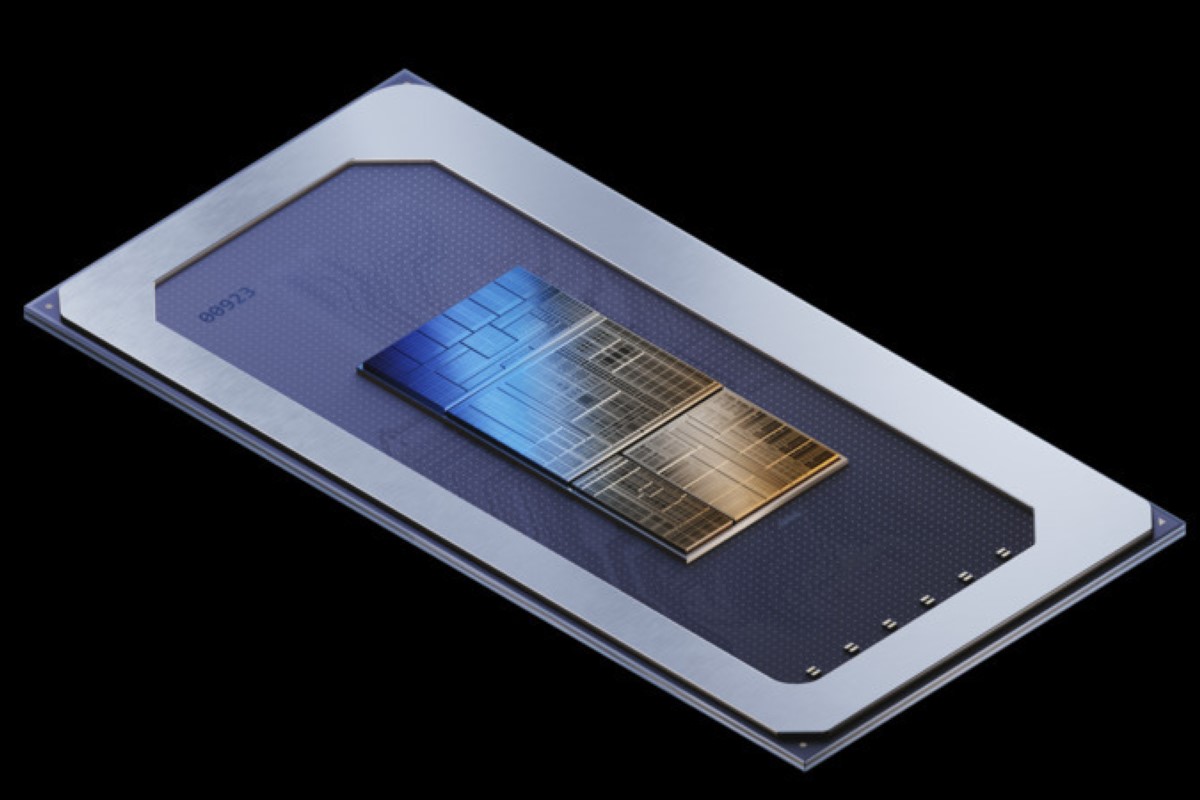

Intel
The highway to Meteor Lake
Traditionally, an Intel CPU has been divided into two principal elements, packaged collectively: the CPU and Platform Control Hub, or PCH. A Direct Media Interface (DMI) bus related the 2. In this scheme, it’s straightforward to think about the association because the CPU, and “everything else”: I/O, reminiscence, and so forth. (It’s not that clear-cut, however you get the concept.)
Intel’s new tiled association solves a number of issues. For one, every tile may be labored upon individually, by itself roadmap, and manufactured on the manufacturing course of it calls for. Intel makes use of its Foveros technology to attach and stack all of them collectively.
After stalling out on a 14nm manufacturing process for years, Intel’s new plan is to regain manufacturing management by striding by means of 5 new manufacturing course of applied sciences in 4 years, sooner than it ever has earlier than. But one of many promoting factors of Meteor Lake — that it’s an “Intel 4” chip — is a trifle misleading. Only the CPU tile is manufactured on Intel 4. In reality, the graphics tile and SOC tiles are fabricated at manufacturing rival TSMC.

Intel
Intel’s new tiles additionally imply that its logic may be intelligently separated from each other, saving energy. Each tile is related by a material that gives roughly 128GB/s of bandwidth.
Intel’s chief government Pat Gelsinger has referred to Meteor Lake as its “Centrino moment,” hearkening again to twenty years in the past when Intel launched the Centrino brand.
Centrino was the primary time that Intel bundled a CPU, chipset, and Wi-Fi chip collectively, however most neglect that it was additionally Intel’s response to Transmeta, a failed CPU startup that provided drastically decrease energy choices for laptops. Intel’s legacy CPU-PCH design meant that just about all duties touched each chips, powering them up into an lively state. Even although Intel then tried to return the CPU and PCH to a low-power sleep state as quickly as doable, it nonetheless was an inefficient use of energy, Intel executives mentioned. By separating Meteor Lake into tiles, Intel can depart the unused tiles in a power-saving deep sleep mode.
According to Michelle Johnston Holthaus, government vice chairman and basic supervisor of Intel’s Client Computing Group, prospects requested for higher energy financial savings. Meteor Lake will ship the efficiency of Raptor Lake (or just a little extra) at roughly half the ability, she mentioned.
“‘We love the performance that Intel delivers, but we want it in a more efficient power envelope and we want a more balanced platform,’” Holthaus instructed PCWorld in an interview, referring to what she mentioned prospects have instructed Intel. “This delivers all that.”
Intel
But there’s additionally an enormous secondary bonus, too: manufacturability. Intel’s Intel 4 course of is the primary to make use of Extreme Ultra Violet (EUV) lithography, a know-how that solves a basic drawback: The transistors that Intel carves out of its photoresistive silicon wafers are smaller than the wavelengths of sunshine used within the etching course of. EUV (which requires a tough vacuum contained in the gear) is seen as the way in which ahead to Intel 4 and past.
Intel doesn’t even manufacture all of its tiles itself. Intel’s Meteor Lake GPU tiles are made by TSMC, in its 5nm N5 course of; the SOC tiles are made by TSMC in its 6nm N6 course of, whereas the CPU tile is made by Intel on its Intel 4 course of. (Intel didn’t say who makes its I/O tile.)
Intel, led by CEO Pat Gelsinger, has pledged to roll out five process technologies in four years, believed to have begun with the Intel 7 course of utilized by the Twelfth-gen Alder Lake chips. The Intel 4 course of additionally makes use of an alloy referred to as enhanced copper, a mixture of copper and cobalt for superior conductivity, Bill Grimm, a vice chairman in Intel’s Logic Technology Development group, mentioned.
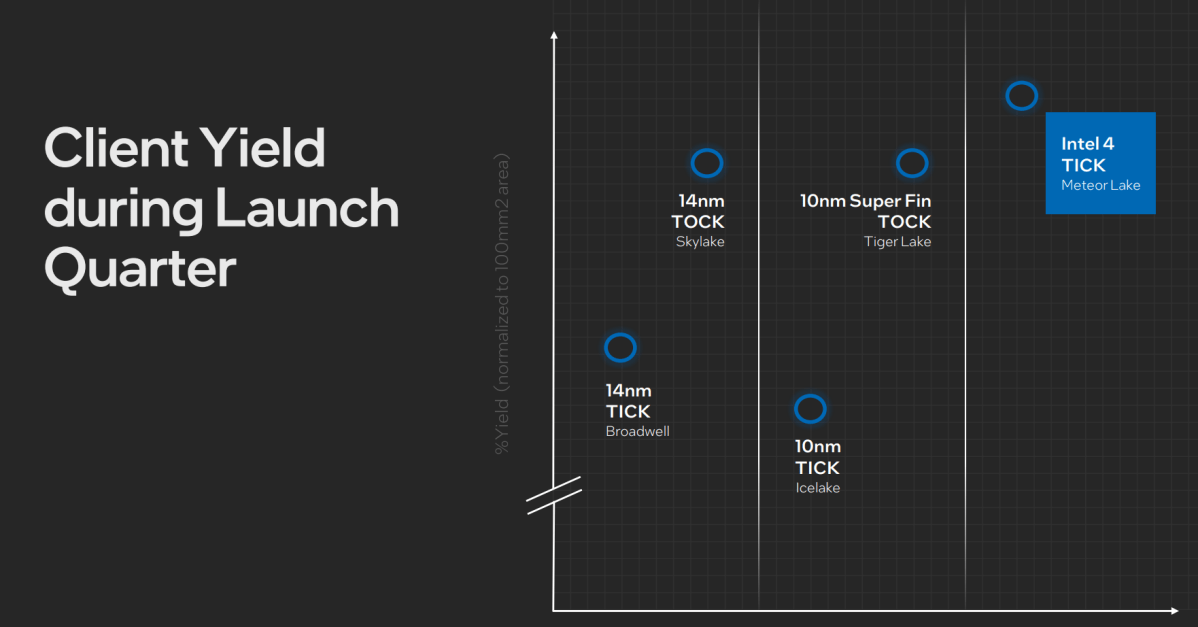
Even higher, Grimm instructed attendees that the smaller tiles additionally imply that they’re simpler to really produce. Small errors within the manufacturing course of could make a chip too flawed to ship (an issue that the iGPU-less Intel “KF” collection was designed to resolve). Smaller tiles additionally imply extra chips may be positioned on a wafer.
Intel
According to Grimm, Meteor Lake will probably be “the best yielding product at time zero [launch] in more than a decade.” Intel expects that Meteor Lake will see higher yields than both any 14nm or 10nm chips, he mentioned. That’s in all probability excellent news for the supply and value at which Intel sells Meteor Lake to laptop computer makers.
Meteor Lake’s CPU tile
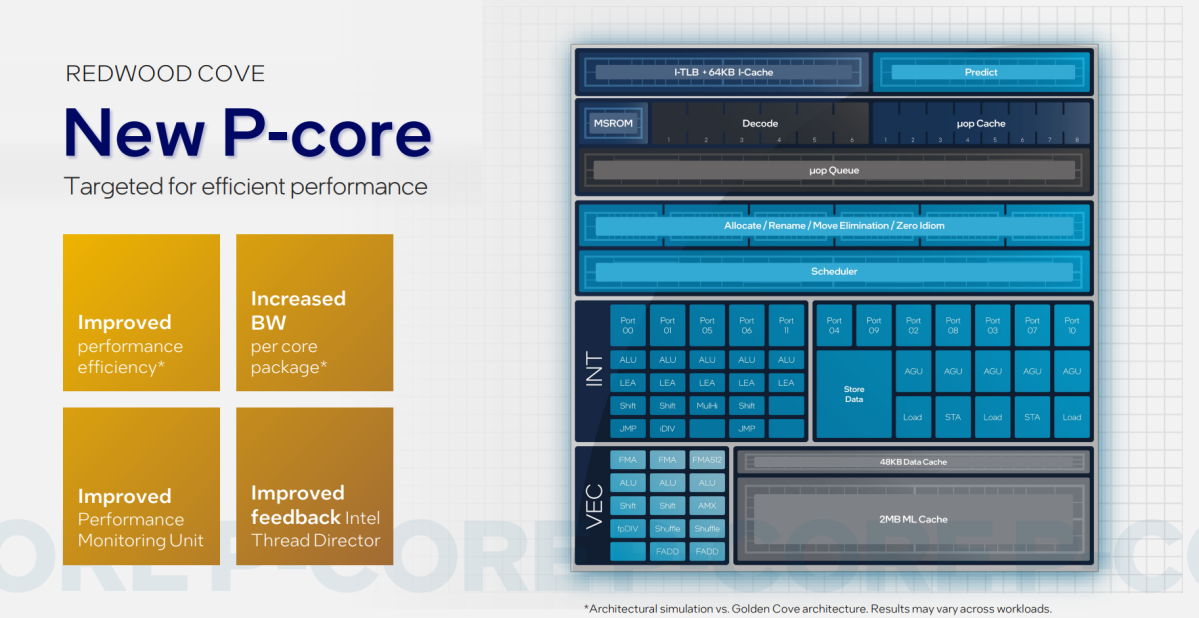
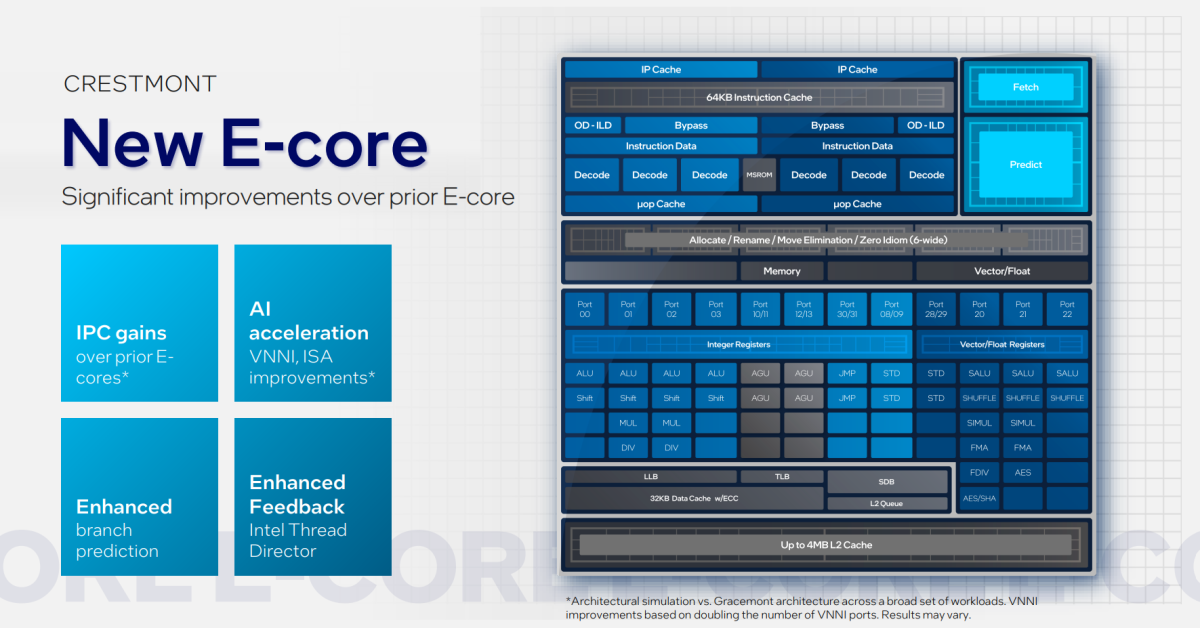
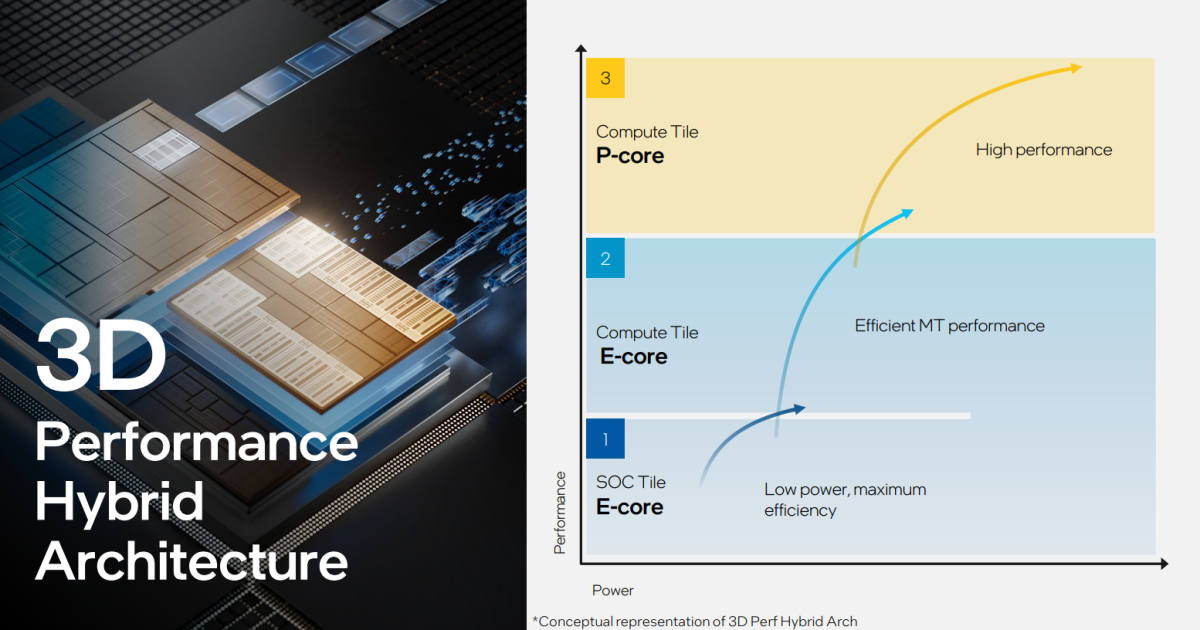
As with the Thirteenth-gen Raptor Lake, Intel’s 14th-gen CPU tiles consists of two main elements: the efficiency cores (P-cores), now often called Redwood Cove, and the brand new effectivity cores (E-cores,) code-named Crestmont.
We actually don’t know that a lot about what variations there are between Raptor Lake’s P- and E-cores and people present in Meteor Lake. Redwood Cove, nonetheless, does supply improved efficiency effectivity and improved bandwidth, with a bigger, although undisclosed level-2 cache.
Intel
Intel additionally didn’t disclose something about Redwood Cove’s efficiency enhancements. Rajshree Chabukswar, an Intel fellow in its shopper programs and software program division, nonetheless, mentioned that Crestmont’s efficiency enhancements are between 4 to six p.c sooner by way of directions per clock versus Raptor Lake. (An IPC enchancment signifies that, if Raptor Lake and Meteor Lake have been to run on the similar velocity, Meteor Lake’s Crestmont E-cores would run 4 to six p.c sooner.)
Intel isn’t revealing the assorted Meteor Lake configurations, but it surely did showcase one throughout its Tech Day presentation.
“For demonstration purposes during our Tech Day presentation, we showed a 6 [P-cores] +8 [E-cores] configuration,” an Intel spokesman confirmed in an electronic mail. “However, we’ll be sharing additional product details closer to launch — including specifications, features, configurations, and performance data.”
Intel
To be truthful, we don’t even formally know if Intel will ship a desktop model of Meteor Lake, which some name Meteor Lake-S. As for a rumored desktop “Rocket Lake Refresh” chip, Intel didn’t disclose that chip’s existence, both. We can hope that Intel provides some further clarifications this week at its Innovation convention.
Meteor Lake’s SOC tile: What low-power E-cores imply to you
One characteristic that’s not on the CPU tile are Meteor Lake’s new low-power E-Cores, and that was a deliberate alternative.
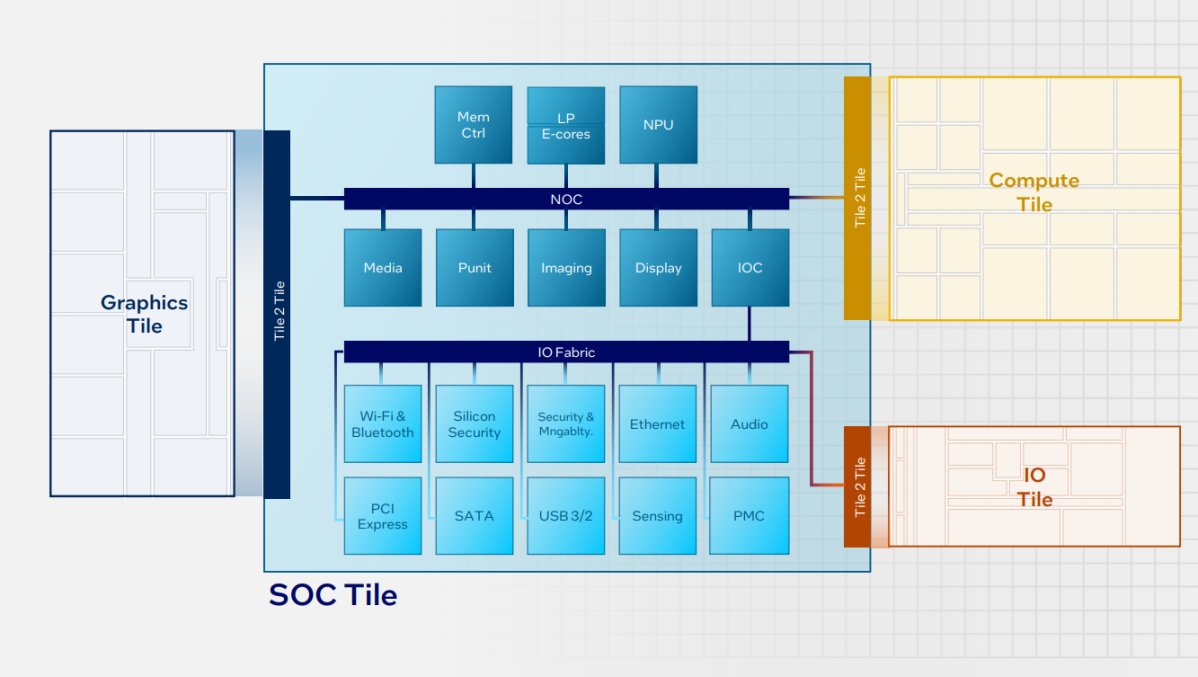
Meteor Lake’s two new low-power E-cores are contained inside the SOC tile, Meteor Lake’s most advanced by way of its array of capabilities. While the CPU tile incorporates the CPU cores, the SOC tile is actually the previous PCH, housing the overwhelming majority of Meteor Lake’s secondary capabilities. Here, you’ll discover the low-power E-cores, the brand new NPU AI engine, in addition to the show engine, PCI Express, and extra.
Intel
Why put low-power E-cores right here? Again, that’s a part of Intel’s low-power plan: By separating the low-power E-cores from the CPU tile, that signifies that solely the SOC tile (or a particular portion of it) must be awoken into an lively energy state. That saves energy, extending the laptop computer’s battery life.
So what’s a low-power E-core? Perhaps just a little lamely, it’s a “new” E-core, a unique model of the Gracemont structure. Recall that E-cores have been initially designed for low-power duties. The new low-power E-cores are designed for what executives known as background “IT tasks,” and it’s not clear what these are, fully. Nor do we all know how “low power” these new cores are.
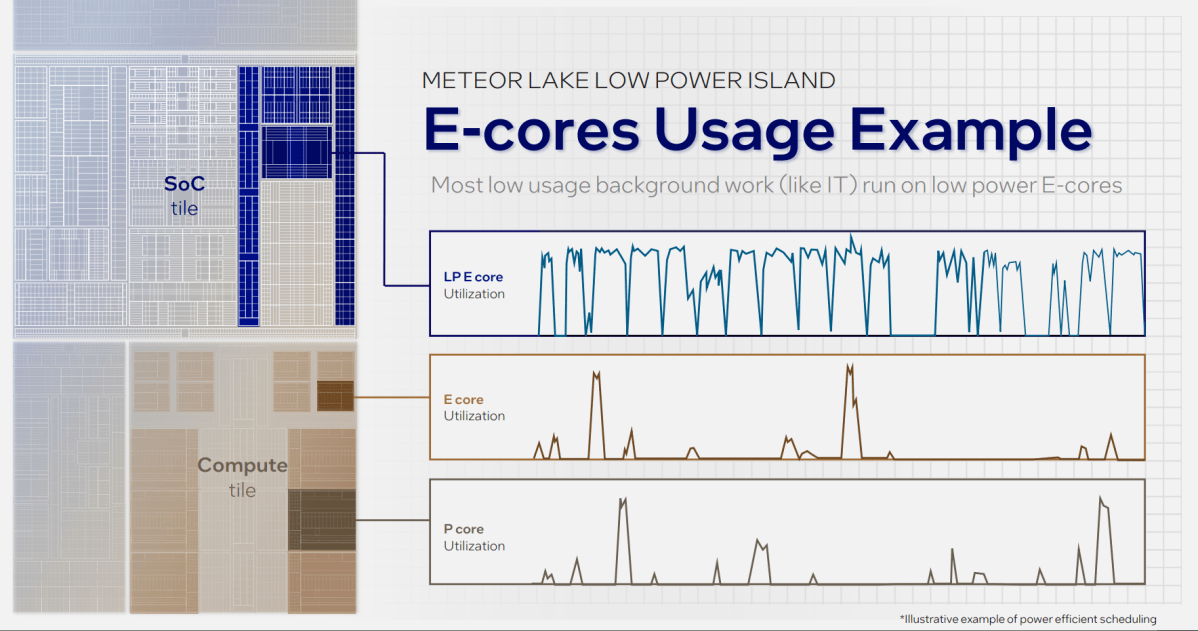
One slightly stunning instance of what these “IT tasks” entail, nonetheless, was when Intel executives used a low-power E-core to play again Tears of Steel, the open-source video file that we use to measure a laptop computer’s battery life. That’s spectacular!
Historically, enjoying again video demanded the eye of the complete CPU up till about 2017. Then, in Lakefield and Alder Lake, Intel started assigning that process to E-cores and P-cores. Now, video playback has migrated to a tiny portion of Meteor Lake. Imagine how typically you play again video. The battery lifetime of laptops ought to improve dramatically simply primarily based upon this process alone.
Intel
Meteor Lake’s Thread Director makes energy, not efficiency, the precedence
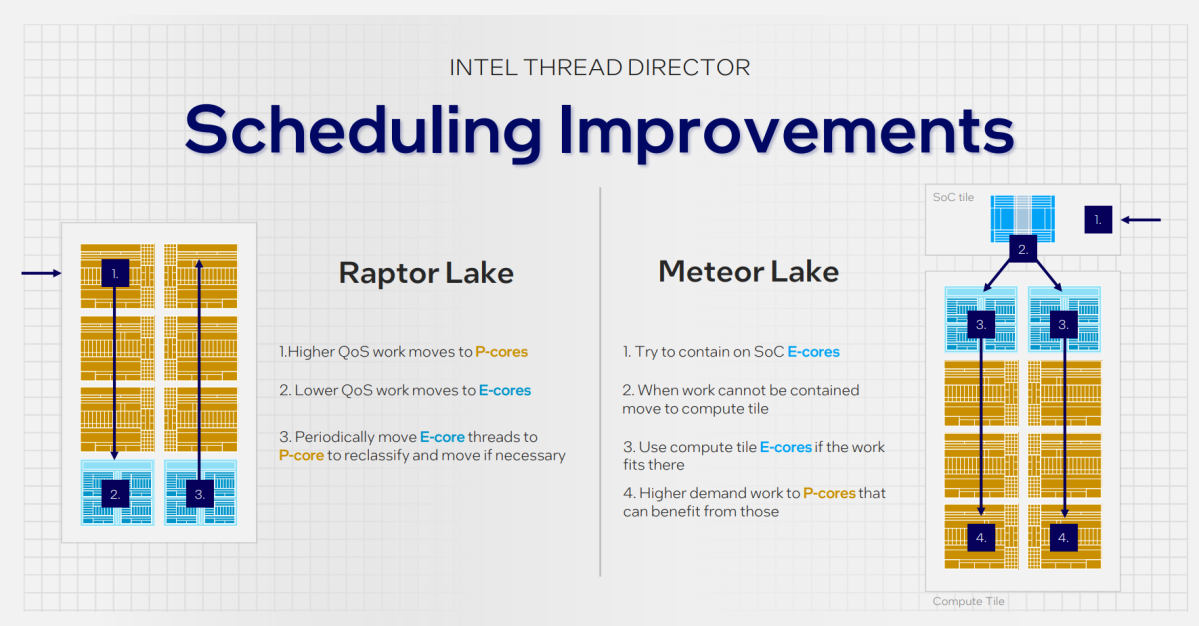
Intel has additionally massively altered Thread Director, the mechanism by which threads or workloads are shunted between cores, inside Meteor Lake. Windows or Linux understands what must be performed and instructs the CPU to take over. That job is then handed to Thread Director. In Thread Director 2, operating on the Core i9-13900K, duties have been routed to the efficiency cores first, then shunted to the E-cores if wanted.
In Meteor Lake, it’s the reverse: Threads are first assigned to the low-power E-cores, then the full-power E-cores, and lastly to the P-cores. Thread Director assigns duties completely different priorities after which assigns the duties accordingly. (The duties are rated not on their efficiency, however by different traits: “0” is “idle,” “2” is “sustained,” and “3” is “bursty.”)
And Intel is severe about this: If a low-power E-core finishes a process and is freed up, an accessible thread will probably be pushed to it, even when a P-core is offered, Chabukswar mentioned. Even in a scenario the place a P-core is free, and Intel’s Thread Director is optimized for efficiency (maybe by way of the Windows power slider), duties will probably be assigned to the E-cores first, she mentioned.
Intel
We’ve gone down this highway earlier than. Though Intel seems to have the ability to modify Thread Director as a coverage, we don’t know whether or not it’s going to. Could a gaming-optimized laptop computer characteristic predominantly P-cores, with Thread Director routing threads to the P-cores first?
Chabukswar agreed that Thread Director may very well be adjusted for the wants of gaming. What isn’t fully clear is whether or not there will probably be a efficiency penalty for beginning a gaming thread, for instance, on a low-power E-core, then stepping it by means of to an E-core after which to a P-core — slightly than recognizing that it wanted a P-core to start with.
Intel already disclosed a few of its power-management plans earlier than in the present day. At the Hot Chips convention in August, Intel disclosed that it would use “AI” on Meteor Lake to find out how a consumer interacts with a standard process like opening an internet web page.
By shortly shifting threads to the fitting cores after which dropping into an idle state, Intel believed it may save 10 to twenty p.c in power with out impacting the consumer expertise. But Meteor Lake gained’t be taught from you: Instead, Intel is taking a median of types from what the machine-learning algorithm has discovered from its take a look at customers.
Intel executives additionally disclosed that they’re working intently with Microsoft, in order that fundamental Windows capabilities may be assigned to the fitting cores.
Meteor Lake’s SOC tile: AI arrives in your PC by way of the NPU
The SOC tile can also be house to what Intel calls the NPU, or AI block. In 2022, Intel CEO Gelsinger confirmed that AI was coming to Meteor Lake, launching the “AI PC era.” According to Holthaus, Intel will ship “millions” of those AI PCs. Incidentally, this NPU will probably be on all variations of Meteor Lake, Intel confirmed.
Intel
Intel is definitely on its third technology of AI: The first technology it bought from Movidius in 2016, later constructing discrete playing cards into some PCs just like the Samsung Galaxy Book3 Ultra that allow these PCs to do background blurring and noise filtering by way of what’s often called Windows Studio Effects. (While Windows Studio Effects use the Movidius know-how, Zoom, Teams, Google Meet, and others merely use your PC’s CPU or GPU as a substitute.)
What Intel is making an attempt to do is place the PC for future AI functions, even when it doesn’t know precisely what they’ll be. Tom Petersen, an Intel fellow, confirmed off Stable Diffusion, an AI artwork generator. He additionally demonstrated a plugin for audio editor Audacity that not solely separated the vocals from the backing devices, however later altered that instrumental fashion utilizing a textual content immediate. Intel’s purpose seems to be the tide that lifts all boats, accelerating AI APIs like WinML, DirectML, and its personal OpenVINO inference engine.
“Our goal is to democratize AI,” mentioned Tim Olson, basic supervisor of SOC design for Intel, in a separate presentation.
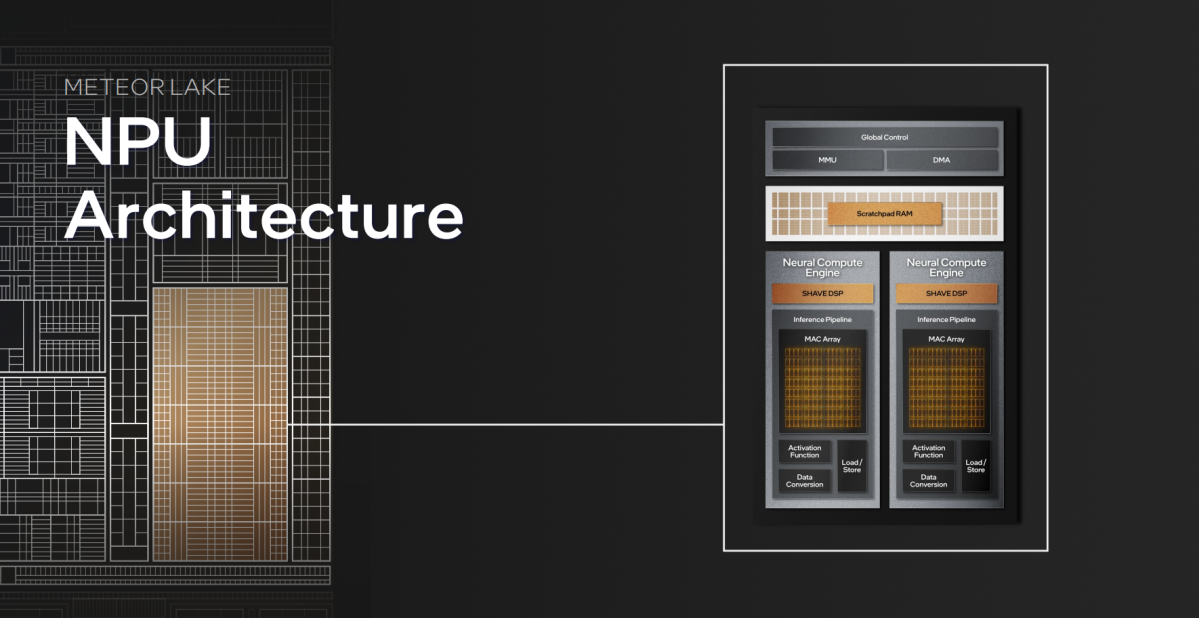
Intel
The NPU is one a part of that. Intel’s NPU features a pair of neural compute engines, every with two VLIW Shade DSPs inside, with inference engines able to as much as eight directions per cycle. Even for customers used to parsing the variety of cores per chip, base clocks, and turbo clocks, this gained’t make loads of sense. What Intel is making an attempt to convey is that AI requires a ton of multiply-accumulate (MAC) directions per cycle, and that these engines can carry out 2,048 MAC calculations every.
Is that good? Is that unhealthy? We actually don’t know. We don’t actually have a basic level of reference for what makes for “good” AI, by way of specs or benchmarks, and Intel executives gave us the concept they’re making an attempt to work that out, too.
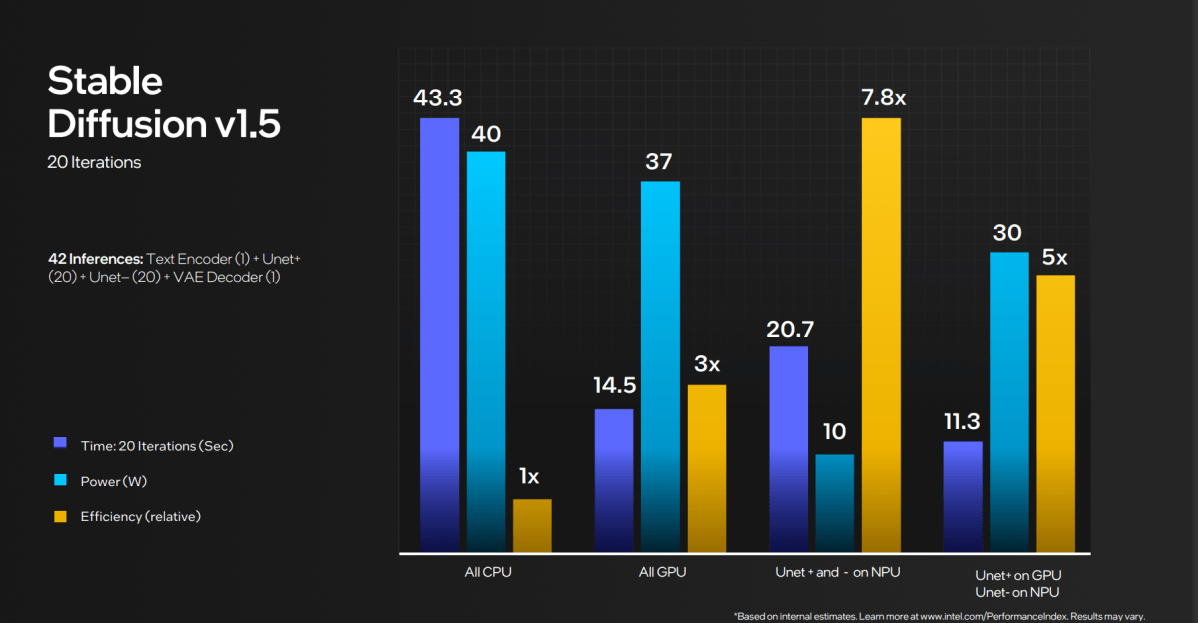
Intel’s secret sauce, although, isn’t simply the AI NPU, however how the CPU, GPU, and NPU can all assist help one another. Take the next instance. Running 20 iterations of Stable Diffusion, Intel tried varied mixtures: performing the entire calculations on the CPU, all on the GPU, all on the NPU, and a mixture of all three. Performing all of them on the NPU took 20.7 seconds and 10 complete watts, essentially the most environment friendly use. But performing all of them on the GPU and NPU completed the duty in 11.3 seconds, consuming 30W.
Which is best? Ideally, the consumer and/or Windows will make that call. But it’s not an easy, easy resolution.
Intel
Intel can also be integrating what it calls the DP4A instruction into the GPU, a GPU instruction particularly designed to speed up AI.
Remember, Intel’s not disclosing all of what Meteor Lake hides. We know, for instance, that PCI Express Gen 5 (PCIe 5) will probably be supported, however not what number of lanes. Ditto for what taste of Ethernet the chip will assist, or the variety of USB bus connections. It seems, although, that the chip will assist Thunderbolt 4, however not the upcoming 80Gbps model, Thunderbolt 5.
Intel executives additionally mentioned that the chip would assist DDR5 and LPDDR5, however we don’t know for sure if that excludes DDR4 or LPDDR4. Intel has confirmed that each Wi-Fi 6e and Wi-Fi 7 will probably be supported, nonetheless, giving gobs of headroom for persistent wi-fi connectivity.
Intel primarily separated the SOC tile into two halves, with an I/O material connecting the entire I/O (Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and so forth) to the I/O tile. A separate NOC material connects the low-power E-cores, NPU, and show controller. (A small I/O controller connects each halves.) Again, this was performed to reduce energy consumption, as every half can work as independently as doable.
Intel’s imaging and show blocks assist HDMI 2.1, DisplayPort 2.1, and embedded DisplayPort 1.4. One necessary characteristic that Intel is disclosing is what number of shows Meteor Lake will assist: as much as a single 8K60 show (with HDR), or 4 4K60 shows, once more with HDR. And should you’re a gamer, Meteor Lake will assist a single 1080p or 1440p show at 360Hz. That’s an enormous deal.

Intel
The media engine will assist 8K60 10-bit HDR decode and encode, with assist for varied codecs. Among them is the open-source AV1 codec, which has already demonstrated impressive encoding results running under Intel’s standalone Arc chip.
Intel additionally put a small twist in its show engine to avoid wasting energy: If the identical body occurs to repeat, Meteor Lake is sensible sufficient that it will possibly depart the body off fully. Two of its 4 show pipelines are additionally optimized for low energy, which Petersen highlighted as a possible resolution for a digital keyboard on a foldable gadget.
Meteor Lake’s graphics tile: Ray tracing in an built-in GPU?
While Intel’s debut in the PC graphics space supplied a welcome third competitor, the corporate’s efforts in each the built-in and discrete graphics market have had their points. Meteor Lake and what Intel calls its XeLPG graphics block mix components of each markets, updating the Xe (or XeLP) built-in GPU that has been inside Core processors for the previous couple of years. Essentially, Intel is taking as a lot as it will possibly from its standalone Arc GPUs and placing it contained in the built-in Meteor Lake GPU.
“We’ve taken all the goodness from our XeHPG architecture and put it into our XeLPG architecture,” Petersen mentioned. Even higher, by inserting graphics on a separate tile, Intel can combine and match graphics efficiency for the promote it’s pursuing, Petersen added.

Intel
According to Intel’s Petersen, Intel is concentrating on twice the efficiency of the sooner Xe core, and twice the efficiency per watt, too. Intel is rising the XeLPG’s clock speeds, dedicating extra silicon to it, and making it extra environment friendly.
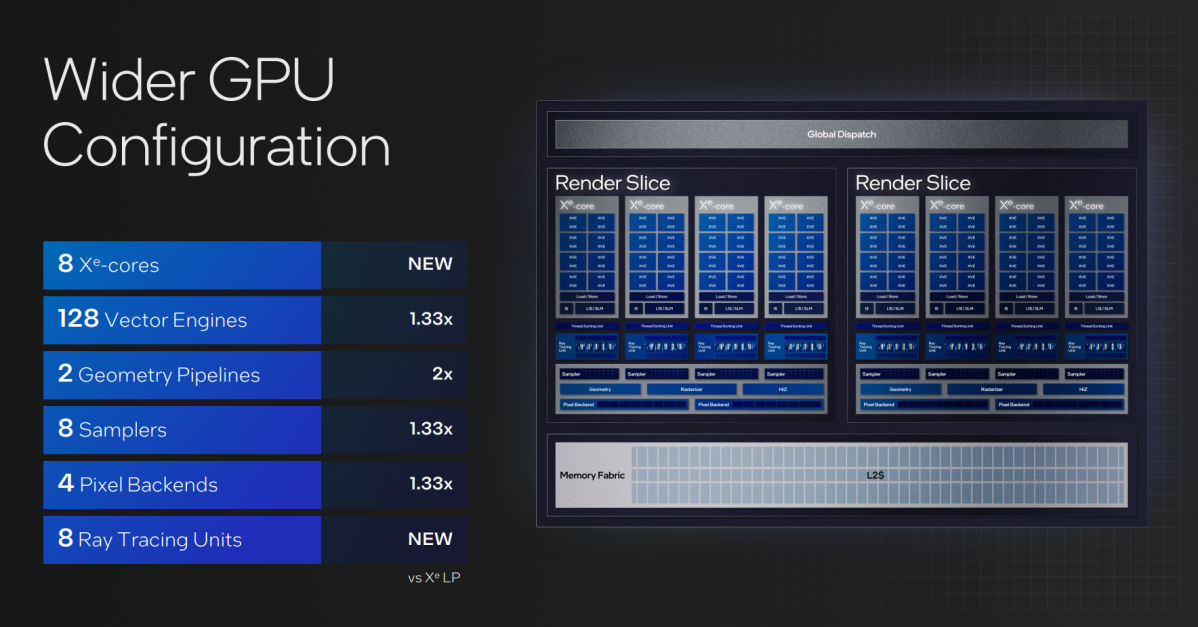
Finally, Intel is bringing within the eight Xe cores from the Arc A770 in addition to eight ray-tracing items into Meteor Lake. Yes, which means ray tracing is now a part of the essential built-in GPU, and never only a discrete chip. Petersen did admit, nonetheless, that it might be as much as software program builders to take benefit.
Intel
Put merely, examine our earlier deep dive into the XeHPG architecture and all of it appears extraordinarily related: Inside every “slice” of the XeLPG core are 4 Xe cores, with 16 256-bit vector engines and 192KB shared L1/SLM cache. Intel helps DirectX 12 Ultimate natively.
There are new bits, too. The new structure helps FP64 directions — Arc doesn’t — plus out-of-order sampling, and Intel’s software program companions instructed Intel that together with FP64 would do wonders for software program compatibility, Petersen mentioned.
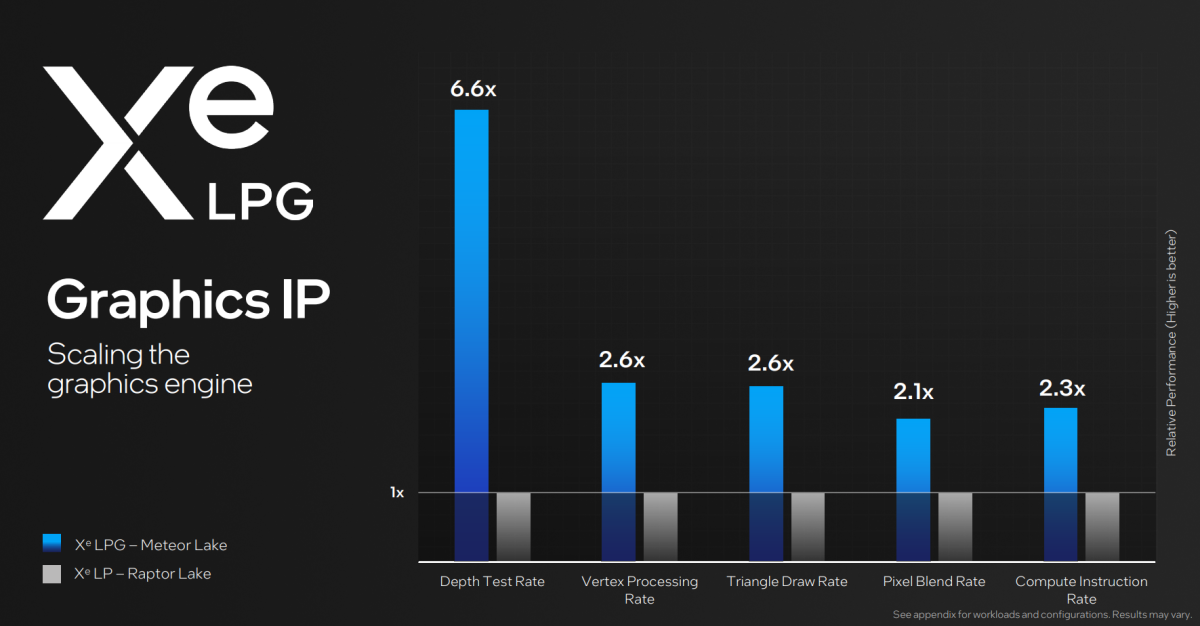
While Intel declined to share precise recreation efficiency information, Petersen did conform to share a few of its “micros,” or inner summary efficiency exams. Measurements starting from triangle draw charge (2.6X over the XeLP present in Raptor Lake) to depth take a look at charge (6.6 occasions Raptor Lake) are one indication that Intel believes that its new Xe cores are head and shoulders above its older know-how. Intel additionally confirmed off Forza Horizon 5 operating on the Meteor Lake {hardware}, however didn’t disclose the decision or graphics settings.
Intel
Meteor Lake’s XeLPG additionally helps XeSS, Intel’s reply to Nvidia’s DLSS. Intel’s know-how renders the body at a decrease decision, then supersamples it as much as a high-res picture.
According to Petersen, this protects power in addition to improves the picture; making use of XeSS lowers the power consumed to 526 millijoules versus 863 millijoules. Meanwhile, Peterson confirmed off body charges that elevated to 1.69X or so when XeSS was turned on.
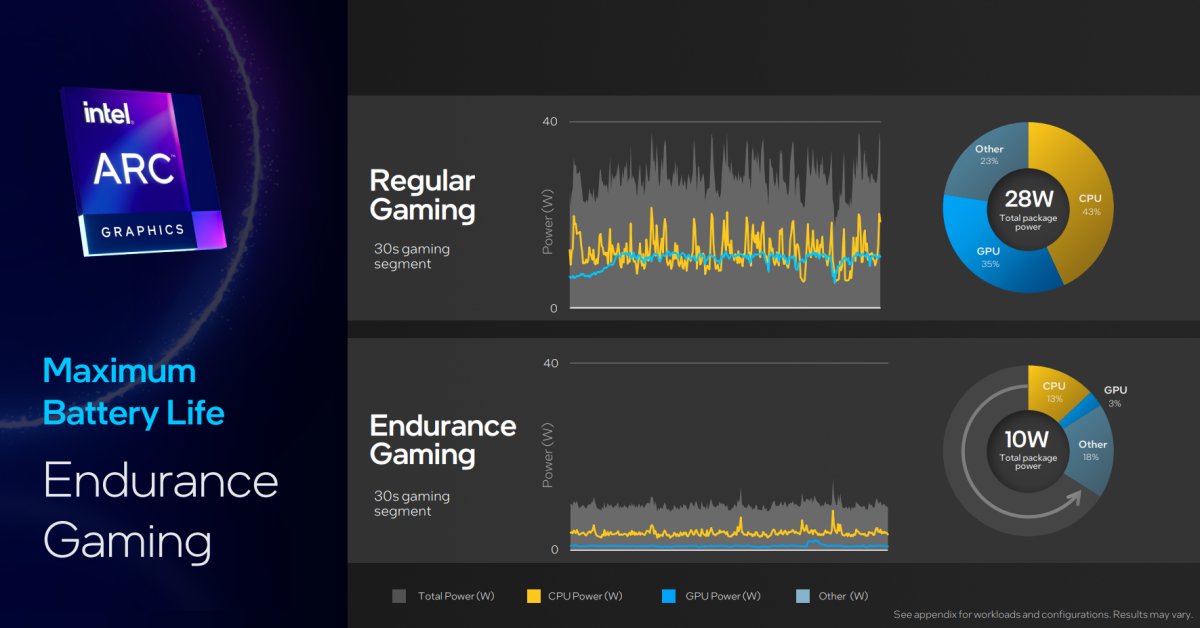
Finally, Meteor Lake introduces what Intel calls Endurance Gaming, which is able to use the Intel Arc Control utility for energy administration. The app talks on to Intel’s cell drivers, moderating efficiency and bettering effectivity; in a “regular gaming” mode, Arc Control, may allocate 28W to the complete system, together with the CPU and GPU. In Endurance Gaming, that may very well be minimize to a complete of 10W, giving simply 1W to the CPU. Intel’s Petersen mentioned that the sport Rocket League may very well be run at 30 frames per second at lower than 1W of energy.
Intel
Appendix: Meteor Lake’s I/O tile
We’re not going to speak in regards to the fourth I/O tile, exactly as a result of Intel barely touched upon it. With many of the “I/O” capabilities really contained inside the SOC tile, among the further, market-specific performance could reside right here. What that will probably be, and what it’s going to seem like, isn’t actually recognized.
Intel confirmed that Meteor Lake can have Thunderbolt 4, not 5, connectivity to external Thunderbolt docks, in addition to exterior USB performance — no surprises there. But Intel fellow Mikal Hunsaker additionally indicated that the I/O tile is also reworked to satisfy the wants of the market.
One query that leaves us with: How shortly will every of those tiles be overhauled? We can’t assist however suppose just a little of how Windows apps like Photos at the moment are on their very own growth cycle, and never tied to any specific Windows launch. It looks as if Intel could undertake an identical method.
Intel’s system-level applied sciences
Intel, naturally, doesn’t simply manufacture PC silicon — its Arc software program is proof of that. But Intel additionally outlined among the system-level initiatives it might deal with with Meteor Lake platforms, too:
Wi-Fi 7: Intel’s BE200 radio chip (aka Gale Peak 2) will probably be used alongside Meteor Lake platforms. It helps Bluetooth LE with decrease energy and latency, in addition to Wi-Fi 7 — with speeds of as much as 5.76Gbps, it’s theoretically sooner than most implementations of wired Ethernet.
Intel Unison: Intel’s Unison software program is like Windows’ personal Your Phone, but it surely’s the best approach to get the iPhone’s iMessage communication in your PC. It’s rather more highly effective with Android, although, and the up to date Unison software program will assist extending your laptop computer’s display screen onto an (Android) pill, in addition to simpler wi-fi communication that may benefit from a number of wi-fi connections.
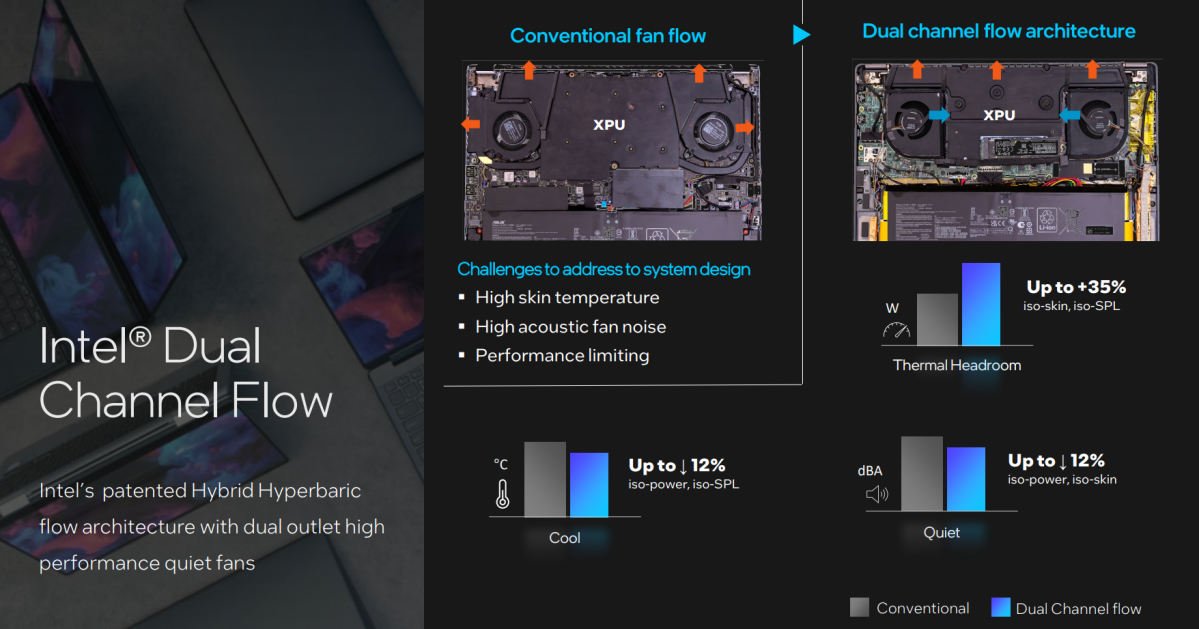
Intel Cool, Quiet, Performant: Part of Intel’s Evo program is working with PC makers to assist co-engineer their notebooks and desktops. Intel confirmed off its dual-channel hyberbaric movement design that it patented, and can be utilized with laptops. It additionally developed an ultrathin vapor channel, additionally patented, that it will possibly provide to pocket book makers. Specific software program to optimize fan velocity and analyze workloads to shift efficiency up and down are additionally choices.
Intel
The fan speeds controls have been designed with acoustics in thoughts, so that they’ll scale up slightly below the purpose the place you’ll discover the fan noise annoying. The workload evaluation software program seems to be, or be associated to, the AI-powered power-management techniques Intel confirmed off beforehand at Hot Chips.
Conclusion
Intel could have introduced us a large quantity of details about its Meteor Lake chip, however we nonetheless don’t know that a lot in regards to the 14th-gen Core: when precisely it’s going to ship, its clock speeds, how it is going to be configured for its varied markets, and so forth. Interestingly, Intel has splintered its Xeon server chip roadmap into two completely different forks: Sierra Forest, made up of all E-cores, and Granite Rapids, consisting of all P-cores. Intel’s tiled structure ought to permit it a few of these choices, if it so chooses.
We nonetheless await AMD’s response within the pocket book house, and even Qualcomm’s reply with its Oryon (Nuvia) technology. But Intel nonetheless ships the overwhelming majority of all laptop computer CPUs, making it the dominant participant within the house. You’ve possible simply learn the particular particulars of your subsequent laptop computer’s microprocessor.
Updated at 9:23 AM on Sept. 19 with further particulars.
(Disclosure: Intel paid for airfare, room, and board on the occasion, which it referred to as the Intel Tech Tour. PCWorld accepted Intel’s supply solely to achieve entry to the occasion. Intel didn’t ask for, nor did PCWorld present, any editorial oversight to Intel representatives.)
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link