
[ad_1]
Intel’s newest 14th-gen Core desktop processors, “Raptor Lake Refresh,” cast off the AI NPU and complicated tiling system contained in the latest 14th-gen “Meteor Lake” cellular chips. But AI is getting used right here, particularly to help what avid gamers care about: enhancing recreation efficiency and CPU clock speeds.
As anticipated, Intel’s “refreshed” Raptor Lake chips provide modest efficiency enhancements over their predecessors, whereas ushering in eventual platform upgrades like Thunderbolt 5. But there are boosts, similar to a tweaked Intel 7 course of that pushes turbo clock speeds as much as 6GHz with the brand new Core i9-14900K and a brand new “Application Performance Optimization (APO)” function that seems to optimize the CPU for a selected recreation.
But — and that is vital, given inflation — Intel is holding pricing (nearly) regular. Prices in Intel’s 14th-gen Core desktop S-series line will vary from $589 for the 24-core, 32-thread Core i9-14900K right down to the $294 14-core, 20-thread Core i5-1400KF, for a complete of six new processors. This is the third straight technology during which Intel has left its processor costs just about unchanged, together with the 13th-gen Raptor Lake and the 12th-gen Alder Lake chip, whose slowest chip was priced at $264.
Perhaps not surprisingly, Intel’s not providing many direct generation-over-generation comparisons with its personal processors, although it chosen just a few content-creation benchmarks to focus on with its Core i7-14700K. There, efficiency enhancements vary from 3 p.c (Adobe Lightroom) to 18 p.c (Autodesk). According to Roger Chandler, vice chairman and basic supervisor of Intel’s fanatic PC and workstation enterprise, the Core i7 options the very best multithreaded efficiency on a Core i7 ever.
Intel executives mentioned the chipmaker had about 130 companions and prospects for the Thirteenth-gen launch, and count on the identical for the debut of the 14th-gen Raptor Lake Refresh chips.
Intel’s 14th-gen Core desktop: Slight pace, core rely will increase
Like Raptor Lake, Intel’s Raptor Lake Refresh is an Intel 7 chip. Otherwise, it’s the identical. Raptor Lake Refresh makes use of the identical die and revision as Raptor Lake; the one distinction is the core rely.
However, Intel has “optimized and refined both our silicon and our process, which has enabled us to get higher frequencies out of the box,” Aarohi Patel, an Intel product advertising engineer, mentioned throughout a press briefing.
Here’s a brief abstract of the brand new 14th-gen desktop Core processors. The barely cheaper -F variants forego the built-in GPU for these prospects who plan to make use of a discrete GPU anyway. All of the brand new these new 14th-gen Core chips run at a processor base energy of 125W.
- Core i9-14900K (8 P-cores, 3.2GHz/5.6GHz; 16 E-cores, 2.4GHz/4.4GHz): $589, $564 for -F variant
- Core i7-14700K (8 P-cores, 3.4GHz/5.5GHz; 12 E-cores, 2.5GHz/5.5GHz): $409, $384 for -F variant
- Core i5-14600K (6 P-cores, 3.5GHz/5.3GHz; 8 E-cores, 2.6GHz/4.0GHz): $319, $294 for -F variant
Both the 14th-gen Core i9 and Core i7 processors enhance over the Thirteenth technology, albeit in numerous methods. All of the Raptor Lake Refresh chips embrace the identical UHD 770 built-in GPU because the prior technology.
It’s not shocking that Intel chosen the Core i7-14700K as some extent of comparability, as that chip reveals essentially the most marked architectural enhancements over the Thirteenth-gen Alder Lake. (“It was where we had the biggest opportunity to add additional cores, so we did,” Chandler mentioned.)
The Core i9-14900K/F stays unchanged at 24 cores and 32 threads; so does the Core i5-14600K, at 14 cores and 20 threads. The new 14th-gen Core i7-14700K/F, nonetheless, consists of 20 cores and 28 threads. That’s a bonus in comparison with the Thirteenth-gen Core i7-13700K/F, which in-built 16 cores and 24 threads. All of the brand new Core i7-14700K/F cores are E-cores.
But the Core i9-14900K/F are the one two chips with an elevated clock pace in comparison with their Thirteenth-gen counterparts: The Core i9-14900K’s P-core clock pace elevated from 3.0GHz to three.2GHz, whereas the E-core frequency elevated from 2.2GHz to 2.4GHz.
Here’s an Intel-supplied diagram of the six new 14th-generation Raptor Lake Refresh processors with extra element.
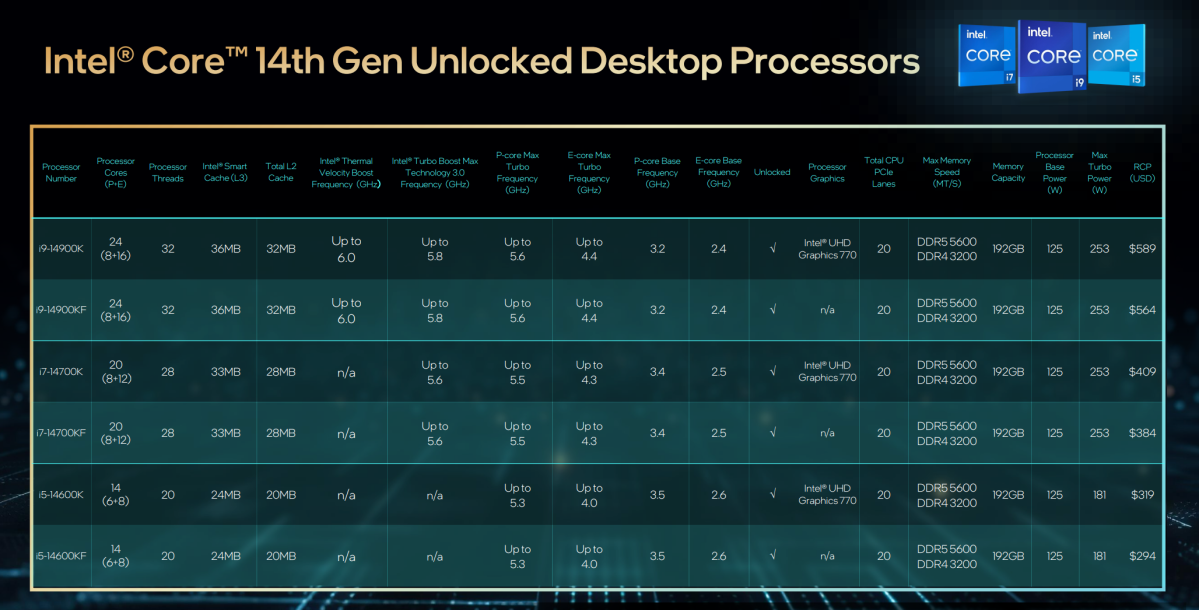
Intel
Remember, Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 identifies the processor’s quickest cores and routes duties to them, particularly very particular single-threaded jobs. Intel Thermal Velocity Boost can apply 100MHz of extra increase clock if the chip’s thermal tolerance can take it — for instance, in case your PC was shut down in a single day and has simply booted. It’s a “bursty” function, although, so it’ll rapidly activate and switch off.
As famous above, the PL1 state (or the quantity of energy the chip consumes usually) is 125W. In its turbo/increase or PL2 state, the chip consumes 253W, the identical as Alder Lake.
Platform enhancements are on the best way
These new 14th-gen Raptor Lake Refresh chips can be backwards suitable with current 600- and 700-series motherboards, so it is best to be capable of slot them into current motherboards with minimal adjustments, apart from the standard BIOS updates. “Generally, it should be a seamless upgrade,” Chandler mentioned.
However, Intel’s Chandler recognized two key forthcoming additions to the 14th-gen platform: Wi-Fi 7, and Thunderbolt 5. Wi-Fi 7 will allow wi-fi speeds that exceed wired throughput at over 40Gbps, and the primary Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) routers are already rolling out. (It’s value noting that Wi-Fi 7 continues to be a “draft” commonplace, which hasn’t been completely ratified, so it is a barely dangerous buy.) Specifically, Wi-Fi 6e can be built-in, whereas motherboard makers who want to add Wi-Fi 7 choices can accomplish that however with a discrete part. (Ditto for Bluetooth; Bluetooth 5.3 is built-in, whereas Bluetooth 5.4, which provides improved one-to-many communications options, requires a discrete chip.) Intel can be utilizing its “Killer” branding on these.
Thunderbolt 5 isn’t fairly right here but, both, but it surely too will provide speeds in extra of 80Gbps — and even as much as 120Gbps — probably changing HDMI and DisplayPort show connectors, and connecting to exterior SSDs and graphics playing cards. It’s anticipated to debut in 2024, nonetheless, after the primary 14th-gen desktop methods have shipped.
However, Intel mentioned after the launch of the 14th-gen Raptor Lake Refresh chips that Thunderbolt 5 wouldn’t be a part of the platform, in any respect. “While some processors in the Intel Core 14th Gen processor family will include support for Thunderbolt 5, Intel Core 14th Gen desktop processors, specifically, will not support it,” a spokesman mentioned in an electronic mail. “However, we’ll be sharing additional details on Intel Core 14th Gen CPUs that support Thunderbolt 5 at a later date.”

Mark Hachman / IDG
What’s attention-grabbing is that Intel apparently expects 20Gbps USB 3.2 (Gen 2×2) to go mainstream as effectively. Though Intel launched this function with Raptor Lake, it’s nonetheless a relative rarity: USB-C ports often provide 10Gbps and that’s it. Why must you care about 20Gbps USB-C? Because that’s just about the standard for external gaming SSDs, which is usually a very enticing product to purchase in case your gaming rig has ever run out of house on the principle drive.
Memory help stays for each DDR4 and DDR5, with as much as DDR5-5600 and DDR4-3200 help for the Core i5, i7, and i9 merchandise, an Intel spokesman mentioned through electronic mail.
Perhaps essentially the most intriguing addition, although, is what Intel calls Application Performance Optimization, or APO. Remember Intel’s Dynamic Tuning Technology? That 2018 expertise dynamically juggled energy between the CPU and the GPU, to eke out as a lot efficiency as attainable. APO sits inside that framework, in response to Intel, and alongside the Thread Director technology that assigns duties to the E-cores and P-cores. (Unlike Meteor Lake, Thread Director returns to the behavior of assigning new duties to the P-cores because it did in Raptor Lake, by the way.) Intel refers to APO as a “scheduling policy.”
What’s the distinction? It’s a bit imprecise. APO can “detect exact application instantiation, and direct and control the thread type,” in response to Patel. Thread Director operates at a better stage, taking path from the working system.
Here’s the underside line: APO is basically like a GPU driver improve for the CPU, permitting what executives referred to as a “nice performance bump” in video games like Metro: Exodus (16 p.c improve) and Rainbow Six: Siege (13 p.c improve), in response to Chandler. While it’s enabled by default, it may be disabled, although it’s not clear what advantages you’d see from doing that.
Intel executives mentioned that there aren’t any unfavourable results from turning on APO. Unfortunately, it’s being tuned for particular video games, and never non-gaming purposes like Photoshop. (That might occur, however there aren’t any ensures.) It may even want particular help from Intel, so video games simply gained’t be enhanced by default. “We see this as an opportunity to actually boost the performance for individual games without having an overall performance impact on other applications,” Chandler mentioned.
Oh, and APO gained’t work with benchmarks, both — or should you or another person adjustments the title of the executable file, Chandler mentioned.
Intel 14th-gen desktop efficiency: Don’t count on an excessive amount of
Since that is “Raptor Lake Refresh,” there aren’t any architectural enhancements; the design of the chips stays the identical, so any enhancements arrive simply in improved clock pace. That implies that efficiency enhancements ought to be minimal.
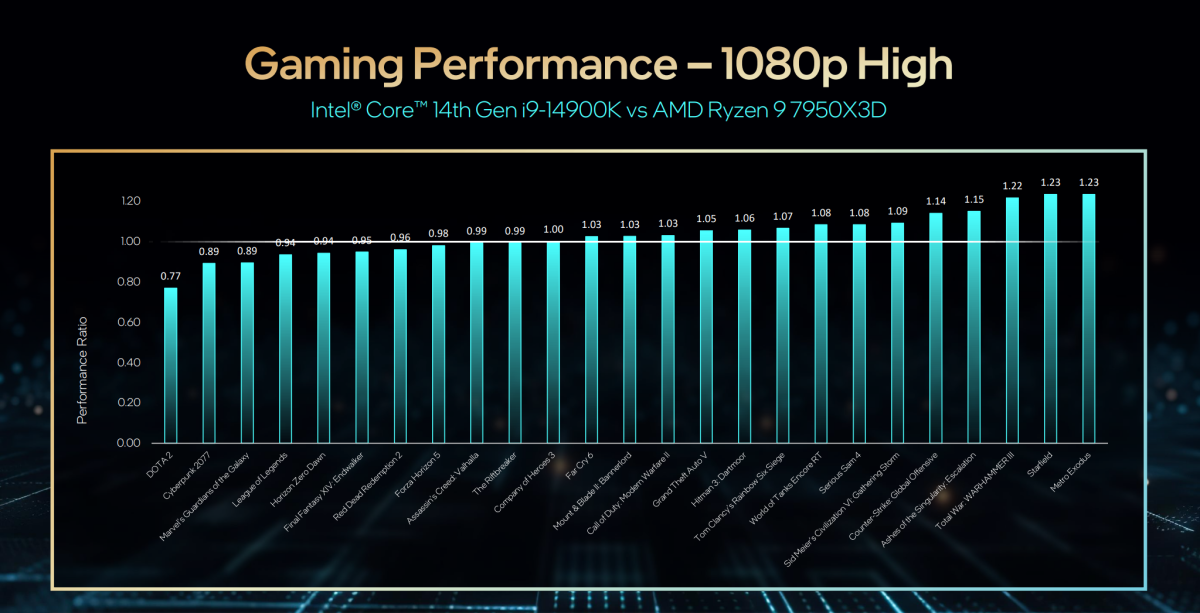
Intel
“There is no architecture change,” Patel mentioned. “So the IPC [instructions per clock] is exactly similar to what we had before.”
Intel, surprisingly, didn’t launch gen-over-gen comparisons for any video games performed on the 14th-gen Core. According to Chandler, the development could be within the “mid single digit, maybe upper single digit” vary, excluding the consequences of APO. Instead, Intel centered on comparisons to the competitors, AMD, and tried to point out the starker demarcation between its Twelfth- and 14th-gen processors as a substitute.
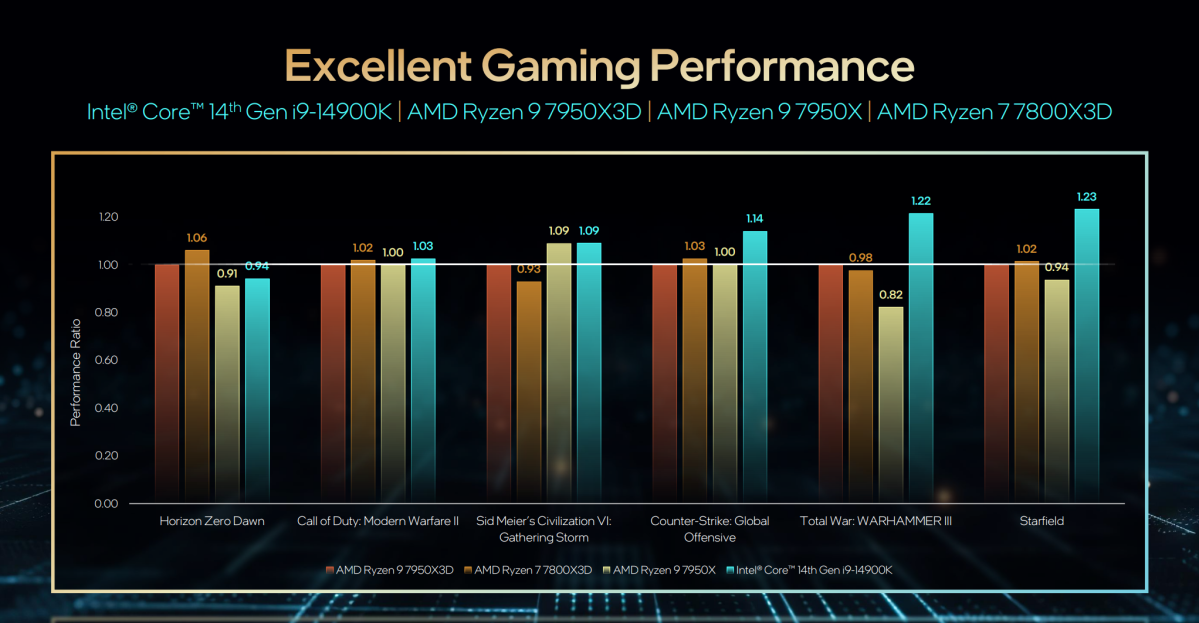
Intel
Intel additionally provided its personal analysis of how its 14th-gen Core i9-14900K compares to the AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D, with modest enhancements throughout the board. It did the identical with a choice of Ryzen 9X and 9X3D chips, as effectively.
As far because the generational enhancements are involved, Intel restricted them to the slide seen beneath. There’s at all times a certain quantity of cherry-picking that goes on with benchmarks, however this appears to be like fairly particular.
Although Intel didn’t immediately examine the Thirteenth-gen and 14th-gen chips, we are able to do the mathematics: That’s a 3.6 p.c improve within the Autodesk workload on the far left, rising to 17.6 p.c (Autodesk) and 15.6 p.c (Adobe After Effects) on the far proper. Most of the generational enhancements, nonetheless, seem a lot nearer.
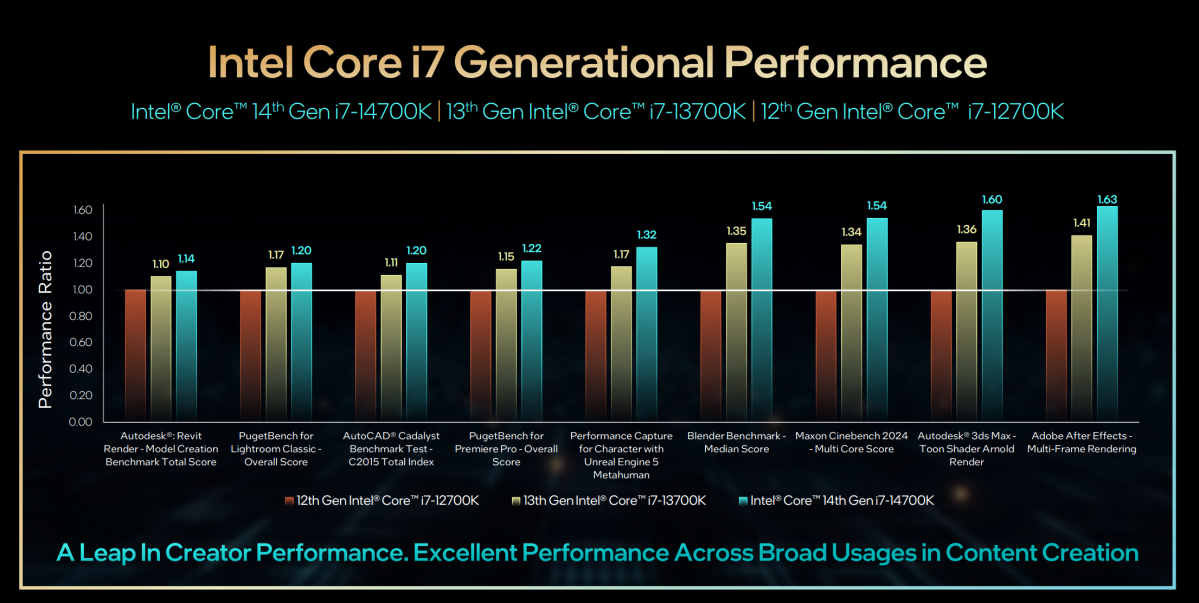
Intel
Overclocking makes use of AI as a weapon
With Raptor Lake, Intel continued to tune its Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU), including one-click overclocking, improved visualizations, and eXtreme Memory Profile 3.0. Now, with Raptor Lake Refresh, XTU is getting private. Intel is including what it calls “AI Assist,” the place AI meets overclocking. AI Assist is a preview function inside XTU, which might be downloaded from Intel’s web site.
AI Assist will basically scan your system, understanding the person elements, voltages, and energy settings and recommending overclocking settings through a “simple step-by-step UI” which might be tailor-made to your system. There is one catch: XTU with AI help can be provided first for Core i9-14900K/KF processors, with help increasing to different 14th-gen unlocked processors sooner or later. It won’t be added to older chips. (On the opposite hand, Intel Speed Optimizer will proceed to be provided alongside AI Assist, in response to Dan Ragland, a principal engineer in Intel’s overclocking lab — which would be the device 14th-gen Core i7 and i5 patrons can use as a substitute.)
The AI Assist device was skilled by machine studying, inferencing a whole bunch of CPUs, plus mixtures of motherboards, coolers, and even customized liquid cooling. All that’s used as a base for its suggestions — although your personal experiences could differ, Intel executives mentioned.
Intel can be providing elevated overclocking frequencies for P-cores and E-cores, greater DDR5 XMP speeds in extra of 8,000 megatransfers per second, P-core thermal throttling, and a third-party overclocking device, FoundationTK.com, that’s based mostly on XTU as effectively.
Ragland, an admitted overclocking fanatic, mentioned that he most well-liked XMP 6600 and two DIMMs per channel for pairing with the brand new Raptor Lake Refresh chips, and patrons will be capable of discover new XMP modules on Intel’s web site at launch. Hopefully, they’ll be as excessive as XMP 8000, he mentioned.
What’s subsequent?
Is Intel doing something greater than treading water? We’ll have to attend for our personal evaluation to see.
However, Intel’s Raptor Lake Refresh doesn’t seem that rather more than simply that — a refresh — however with some attention-grabbing approaches to eking out additional efficiency enhancements via AI. Whether or not this leaves the door open for AMD to reply is one thing we’ll should study within the coming months.
This story was up to date at 9:37 PM to notice that Thunderbolt 5 won’t be a part of the 14th-gen Core desktop platform.
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link