
[ad_1]
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a precedence pathogen for international management. A rising variety of nations have begun to include routine whole genome sequencing (WGS) to help key points of tuberculosis (TB) public health and scientific observe, together with monitoring of laboratory and scientific practices, detection and surveillance of drug resistance, and steerage of focused public well being interventions akin to expanded contact investigation and lively case discovering. However, enhanced constructions, workforce capability and monitoring programs are required to help efficient translation of pathogen genomics into scientific and public well being observe. We take into account key components for embedding WGS into routine TB service supply.
Quite a lot of WGS implementation fashions exist, with most providers initially established with analysis grants or different short-term venture funds. However, given the necessity to construct a talented multidisciplinary workforce and sustainable laboratory providers, dependable long-term funding is important. Multidisciplinary staff members ought to embody experience in mycobacterial diagnostics, tradition and genomics, superior bioinformatics, and geospatial mapping, linking intently with clinical medicine and affected person care, discipline epidemiology, public well being and well being coverage. Programs additionally want steerage from social work, ethicists and context-specific cultural staff, and may actively interact TB affected communities when reviewing obvious clustering and planning precision public well being responses.
The incorporation of WGS information into public well being applications will introduce change on the micro (particular person), meso (inhabitants) and macro (coverage) levels¹ (Fig.1). At a micro stage, genomic information permits recognition of doable person-to-person transmission² and will determine cases of laboratory contamination, permitting pointless treatment to be discontinued.³ Rapid genotypic identification of drug resistance informs personalised affected person administration, whereas WGS clustering identifies transmission and guides higher focused public well being responses, notably in low incidence settings the place transmission is unusual.⁴
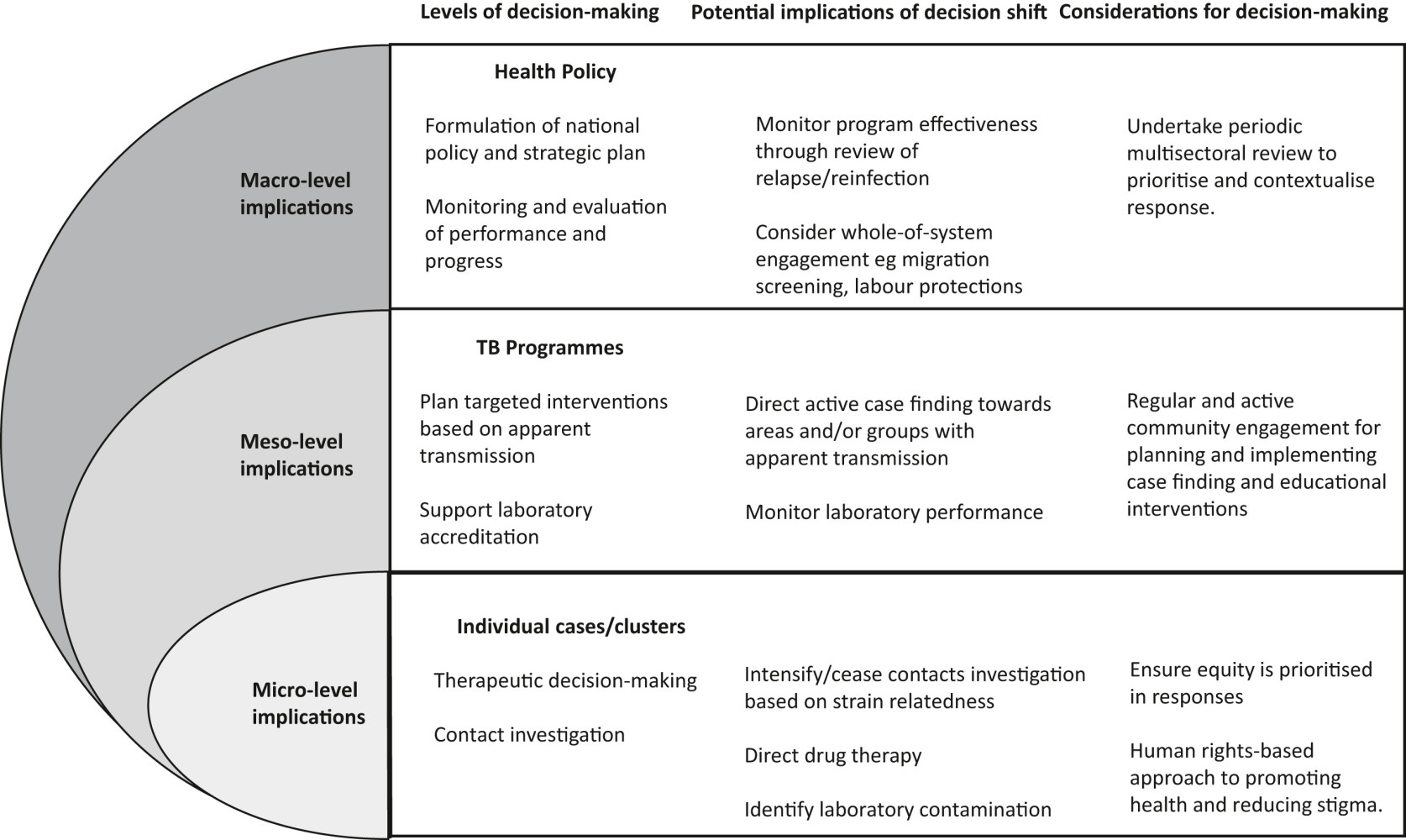
Fig. 1. Levels of decision-making and examples of public well being software of M tuberculosis entire genome sequencing. Adapted from Sawatzky R, Kwon JY, Barclay R et al. Implications of response shift for micro-, meso-, and macro-level healthcare decision-making utilizing outcomes of patient-reported consequence measures. Quality of Life Research. 2021; 30:3343–3357.
Beyond particular person treatment and transmission analysis, WGS info needs to be mixed with broader epidemiological information to guage rising tendencies in drug resistance, carry out larger stage transmission monitoring and assess geospatial ‘hot spot’ distribution. This meso-level evaluation can inform program–stage actions. For instance, genomic information might determine underappreciated TB transmission in individuals from the identical cultural background, geographic space or shared leisure actions not recognized by normal epidemiological analysis.⁵ Such info might information lively case discovering or use of preventive remedy, in addition to the supply of culturally acceptable schooling and data to entry tuberculosis providers.
At the macro stage, WGS information may form TB program and well being service coverage and observe. Different epidemiological contexts might restrict formulation of common targets, however serial analysis can present helpful metrics for service enchancment. Adopting a regular method to such evaluation, akin to monitoring the proportion of instances clustered utilizing a 5-SNP threshold over a 5-year rolling common, will facilitate benchmarking between related contexts and programmatic evaluate of tendencies over time.⁶ However, associating transmission clusters with potential discriminatory components akin to nation of birth, geographical location or behavioral traits might lead to harms to affected communities, which needs to be rigorously thought of.⁷
Public health genomics often lacks sturdy measures for evaluating impression.⁸ While well timed genomic sequencing might have scientific and public well being profit, higher structured multimodal analysis approaches would add worth. This analysis ought to embody evaluation of epidemiological impression of public well being interventions in addition to fairness in key teams affected by TB, and well being financial evaluation, ideally incorporating public well being and patient-level prices, quite than simply laboratory prices. Assessing the significance and acceptability to sufferers and affected communities utilizing co-design approaches can also be vital as are qualitative measures contemplating impression on coverage and observe, akin to use by clinicians and public well being officers to tell therapy and isolation choices primarily based on WGS findings. Despite decreasing prices, the monetary and infrastructure necessities of WGS stay prohibitive for lower-resource settings, particularly given present reliance on culture-based pathways for WGS. Concerted efforts are required to extend the entry that lower-resource settings, which are sometimes excessive TB incidence settings, must probably the most related and domestically helpful WGS advances.⁹ Ongoing growth and routine use of WGS in high-resource settings ought to embody lively help for its international implementation, with an emphasis on equitable entry to its particular person and public well being advantages.
There is nice potential profit from elevated sharing of genomic information between jurisdictions and businesses. However, such exchanges are related to possession and privateness considerations,¹⁰ and in addition require higher standardization to facilitate information comparability and change. Establishing information sharing agreements and customary pipelines is useful however wants to make sure information safety and should appropriately steadiness advantages and burdens. A sturdy authorized framework can also be important, recognizing growing requests to supply such information to help with each private and non-private investigations.
In conclusion, the mixing of routine WGS into TB management responses supply potential for important profit, however considerate software and analysis is required to optimise public well being worth and to make sure that communities affected by TB stand to learn from these advances.
This article was first revealed by The Lancet Regional Health – Western Pacific
References
-
R. Sawatzky, J.Y. Kwon, R. Barclay, et al.
Implications of response shift for micro-, meso-, and macro-level healthcare decision-making utilizing outcomes of patient-reported consequence measures
Qual Life Res, 30 (2021), pp. 3343-3357
-
R. Jajou, A.D. Neeling, R.V. Hunen, et al.
Epidemiological hyperlinks between tuberculosis instances recognized twice as effectively by entire genome sequencing than standard molecular typing: a population-based examine
PLoS One, 13 (4) (2018), Article e0195413
-
A. Kizny Gordon, S.Y. Tong, E. Martinez, T. Crighton, J.T. Denholm, V. Sintchenko
TB genomic surveillance and information sharing in recognising contamination occasions
Int J Tubercul Lung Dis, 25 (3) (2021), pp. 241-243
-
Okay. Dale, M. Globan, Okay. Horan, et al.
Whole genome sequencing for tuberculosis in Victoria, Australia: a genomic implementation examine from 2017 to 2020
Lancet Reg Health Western Pac, 28 (2022), Article 100556
-
C. Yang, L. Lu, J.L. Warren, et al.
Internal migration and transmission dynamics of tuberculosis in Shanghai, China: an epidemiological, spatial, genomic evaluation
Lancet Infect Dis, 18 (7) (2018), pp. 788-795
-
X. Zhang, E. Martinez, C. Lam, et al.
Exploring programmatic indicators of tuberculosis management that incorporate routine Mycobacterium tuberculosis sequencing in low incidence settings: a complete (2017–2021) affected person cohort evaluation
Lancet Reg Health Western Pac, 41 (2023), Article 100910
-
F. Saeed, R. Mihan, S.Z. Mousavi, et al.
A narrative evaluate of stigma associated to infectious illness outbreaks: what might be realized within the face of the Covid-19 pandemic?
Front Psychiatr, 11 (2020), Article 565919
-
A.S. Ferdinand, M. Kelaher, C.R. Lane, et al.
An implementation science method to evaluating pathogen entire genome sequencing in public well being
Genome Med, 13 (2021), p. 121
-
P.M. Pronyk, R. de Alwis, R. Rockett, et al.
Advancing pathogen genomics in resource-limited settings
Cell Genom, 3 (Suppl 1) (2023), Article 100443
-
J.S. Berg, M.J. Khoury, J.P. Evans
Deploying entire genome sequencing in scientific observe and public well being: assembly the problem one bin at a time
Genet Med, 13 (6) (2011), pp. 499-504
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link