
[ad_1]
In the eighties, laptop processors grew to become quicker and quicker, whereas reminiscence entry occasions stagnated and hindered extra efficiency will increase. Something needed to be performed to hurry up reminiscence entry and make the entire system work extra effectively.
The discrepancy between computational and reminiscence pace in the end led to the event of processor cache. Basically, the cache is a quick sort of reminiscence. It incorporates a small space of reminiscence with the directions that the pc will almost definitely want subsequent whether it is to carry out sure duties.
The system masses this info into the cache utilizing complicated algorithms. The major goal of a cache system is to make sure that the processor has quick and on the spot entry to the information it wants in the proper order.
Further studying: The best CPUs for gaming
To perceive how they work, you first have to know that PCs work with three several types of reminiscence: The first is the first reminiscence within the type of a tough disk (HDD) or SSD (Solid State Disk). This is the reminiscence with the biggest capability. Then comes the primary reminiscence (RAM), which is so much quicker, but in addition smaller than the first reminiscence.
Last however not least, there may be additionally reminiscence throughout the processor — the cache. It is the kind of reminiscence that works the quickest. As quickly as a program begins, it executes a collection of instructions that may be discovered within the software program’s code. The program first masses these instructions into RAM, from the place they’re transferred to the CPU. For the absolute best execution of those directions, the processor wants very quick reminiscence. This is the place the cache comes into play.

The cache is a short lived knowledge retailer positioned immediately on the processor. It is used to extend the processing effectivity of the processor by holding continuously requested bits of information able to be retrieved at excessive pace.
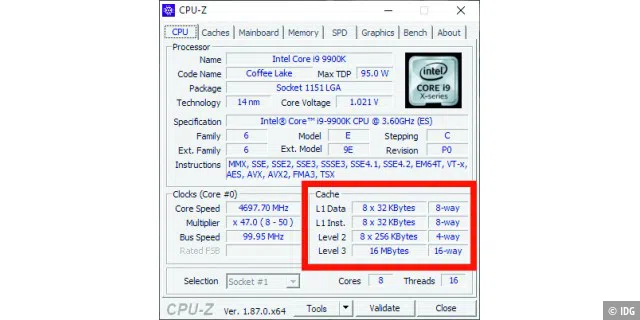
Cache reminiscence consists of various ranges known as L1, L2, L3 and infrequently L4, which differ in location, pace and measurement. The cache reminiscence is extraordinarily quick and positioned as shut as potential to the processor cores. Modern, quick CPUs aren’t slowed down by requests for knowledge from the comparatively gradual system reminiscence (RAM). Instead, they will retrieve the information from the cache.
The L1 cache, additionally known as the first cache, is the smallest and quickest reminiscence degree. It is often 64 KB per core, so {that a} quad-core CPU, for instance, has a complete of 256 KB.

A CPU often has three cache reminiscence ranges. They aren’t the main target of latest purchases, though they’re an necessary side of the CPU structure.
AMD
The L2 cache is the secondary reminiscence cache that can be embedded in every particular person core of the CPU. It virtually at all times has extra reminiscence than the L1 cache, however operates at a slower pace, though nonetheless considerably quicker than major system reminiscence. Some high-end processors can have a complete of 32 MB of L2 cache, however 6 to 12 MB is the common.
Now for the third cache: Unlike the L1 and L2 caches embedded in every CPU core, the L3 cache serves as a shared reminiscence pool that may be accessed by your entire processor. It is way slower than the L1 and L2 cache ranges — and often solely twice as quick as RAM. At the identical time, it’s the largest of all three reminiscence ranges. If the CPU can’t discover the information it wants within the cache reminiscence, it should request the information from the slower system reminiscence as an alternative. This is known as a cache miss.
On the query of whether or not the cache may be cleared manually: Basically, there are reminiscence caches that may be cleared or flushed, such because the system cache or the browser cache. However, you can not actively delete the CPU cache reminiscence. The purpose: It is a unstable reminiscence. This signifies that it doesn’t retain its contents in the long run.
As quickly as you turn off the pc, the content material in your processor’s cache reminiscence is misplaced. As with most varieties of reminiscence, the extra cache a CPU gives, the higher. You can’t improve cache reminiscence, so it’s necessary that the processor you select has sufficient reminiscence out there.
But that is determined by what you do together with your laptop. At the identical time, you shouldn’t focus an excessive amount of on this one CPU function. Clock speeds, the variety of cores in addition to threads and different elements affect CPU efficiency extra.
Each CPU core has its personal cache reminiscence (L1 and L2). The L3 cache is shared by all cores – it’s the largest, but in addition the slowest of the three reminiscence ranges.
Intel
A very good base for the L1 cache is 64 KB per core. You can discover this out by dividing the whole quantity by the variety of cores within the CPU. A 256 KB L2 cache per core is completely acceptable, however players may profit from 512 KB per core. And something between 32 and 96 MB of L3 cache is completely advantageous for many functions.
In abstract, cache reminiscence is an indispensable a part of trendy CPUs. Although the variations between L1, L2, and L3 appear complicated at first look, they assist to maximise the effectivity and efficiency of a pc. If you’re within the course of of buying a CPU, it’s advisable to think about cache as an necessary side of the processor structure.
This article was translated from German to English and initially appeared on pcwelt.de.
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link