[ad_1]
For some time vitamin D was wanting like a bona fide well being elixir. It was acknowledged a century in the past because the treatment for rickets, a childhood illness that causes weak and deformed bones. Then, within the early 2000s, researchers started amassing a pile of research suggesting that low vitamin D ranges might be a consider most cancers, heart problems, dementia, despair, diabetes, autoimmune illnesses, fractures, respiratory sicknesses and Parkinson’s illness. It appeared cheap to suppose that elevating our ranges of this straightforward vitamin—one which our our bodies make when lit up by sunshine and that we will get extra of from dietary supplements—may treatment virtually no matter ailed us.
At least two books referred to as The Vitamin D Cure had been revealed, together with different books and information experiences whose titles embrace phrases like “revolution” and “miracle.” There was additionally a rising concern that we weren’t getting sufficient of the vitamin. Good Morning America aired a section that started with reporter Diane Sawyer declaring 100 million Americans had been poor. Her visitor was Dr. Oz, who advised viewers they may decide their vitamin D degree with a easy blood take a look at. Sunshine is one of the simplest ways to get this vitamin, he mentioned. But if that wasn’t sufficient, he suggested cod liver oil or dietary supplements.
Numerous celebrities and vitamin corporations raised hopes that vitamin D might be a panacea, says JoAnn Manson, an endocrinologist and epidemiologist at Harvard Medical School and a lead investigator on a few of the largest vitamin D research to this point. Sales of dietary supplements containing the vitamin soared, as did charges of vitamin D testing.
Then the underside fell out. Although hundreds of research had linked low ranges of vitamin D to an assortment of medical circumstances, when scientists tried administering it as a method to stop or deal with these issues, the surprise complement failed miserably. The notion that our lives can be higher if all of us simply raised our vitamin D ranges started to appear to be a fantasy. The concept that vitamin D deficiency was widespread additionally crumbled. It turned out that notions of what constitutes a deficiency had been primarily based on a doubtful understanding to start with. National inhabitants sampling confirmed that most individuals had been already getting sufficient of the vitamin.
There’s no query that vitamin D performs an essential position in well being. It helps your physique take in and retain calcium and phosphorus; each are crucial for constructing bone. But apart from a couple of subsets of the inhabitants (akin to breastfed infants and other people with specific medical circumstances), most individuals most likely do not want dietary supplements.
The story of how vitamin D was found, rocketed to miracle standing after which returned to Earth illustrates the generally jagged path of scientific discovery. It’s additionally a cautionary story about the necessity to interpret scientific outcomes with humility. Ultimately it is in regards to the self-correcting nature of science and the way information turns into honed over time.
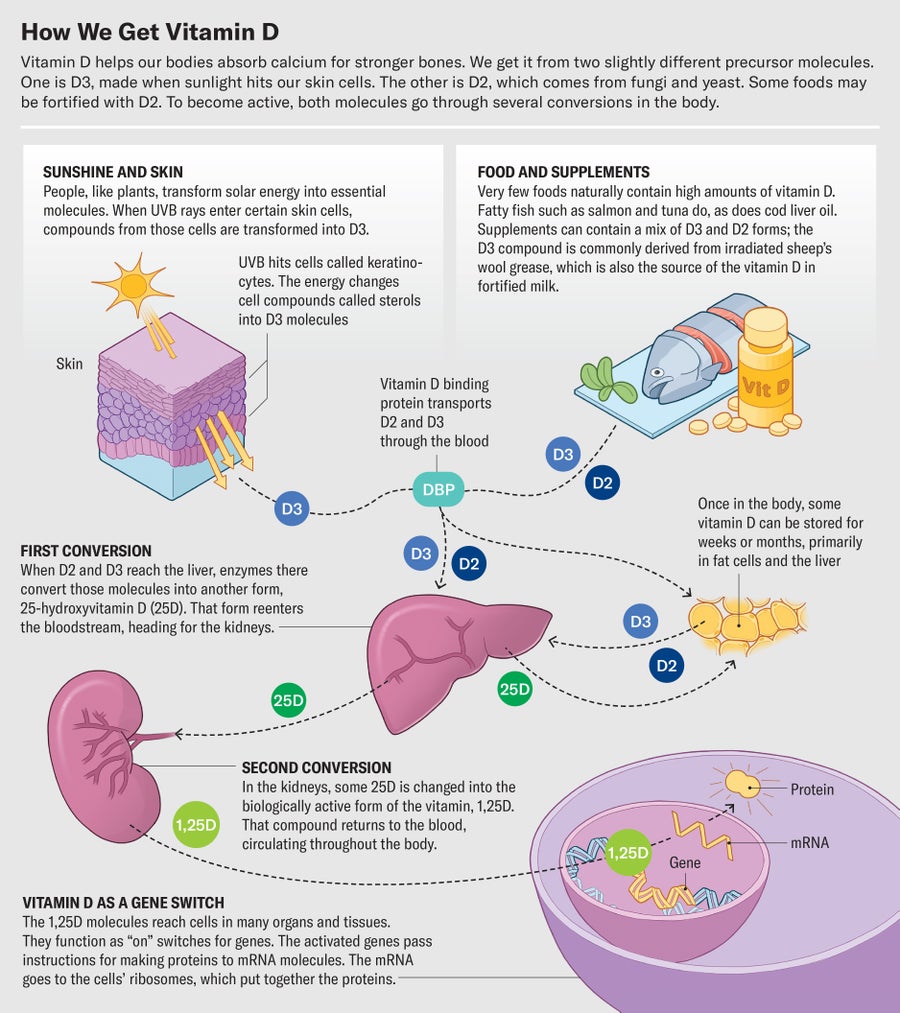
For a lot of human historical past, individuals bought their vitamin D principally from the solar. It seems people are slightly bit like crops—we will flip ultraviolet mild into one thing our our bodies want in a course of akin to photosynthesis.
When the high-energy rays of UV mild—UVB—hit your pores and skin, they begin a sequence response that converts a compound in your pores and skin referred to as a sterol right into a vitamin D precursor. This molecule, after a couple of extra steps, turns into a type of the vitamin that promotes calcium absorption from the intestine and will increase bone mineralization. Vitamin D additionally appears to bolster the immune system and tamp down irritation. It does this stuff partially by influencing the manufacturing of inflammatory compounds and suppressing the buildup of proinflammatory cells. Researchers are finding out whether or not vitamin D can stop harmful inflammatory reactions in individuals with COVID.
Producing vitamin D grew to become more and more tough for human our bodies throughout the Industrial Revolution, when smoke and soot darkened the skies and youngsters spent extra time within the shade of crowded cities, resulting in a rise in rickets. By the late 1800s researchers had documented geographic variations within the prevalence of rickets that pointed to a attainable hyperlink to daylight.
In the Nineteen Twenties Johns Hopkins University biochemist Elmer McCollum recognized vitamin D in cod liver oil and gave it its identify. German chemist Adolf Otto Reinhold Windaus received a Nobel Prize in 1928 for exhibiting how the physique made vitamin D from daylight. Calling this beforehand unknown substance a vitamin gave it a sheen of beneficence. The time period “vitamin” had been coined by Polish scientist Casimir Funk, who created the phrase by combining the phrases “vita” (Latin for “life”) and “amine” (for amino acids, constructing blocks of life). The phrase created “an aura of safety and health,” says Catherine Price, creator of Vitamania: How Vitamins Revolutionized the Way We Think about Food.
The apply of fortifying meals with vitamin D started when McCollum’s former pupil Harry Steenbock, then on the University of Wisconsin–Madison, found that he may produce vitamin D in each rats and their feed by irradiating them with UV mild. The rays hit sterol compounds, discovered within the cells of crops, animals and fungi, and begin a conversion course of. For occasion, exposing chickens to UVB mild boosts the vitamin D of their meat and egg yolks. Most of the vitamin D in fashionable dietary supplements comes from irradiated lanolin, a grease derived from sheep’s wool. Steenbock additionally discovered that feeding dairy cows irradiated feed or mixing irradiated fats extract into milk raised D ranges. Today fortified milk and different dairy merchandise—which additionally use the lanolin-derived type of the vitamin—are a few of the most typical dietary sources.
In 1936 the Joseph Schlitz Brewing Company launched “Sunshine Vitamin D” beer. The adverts exclaimed that “beer is good for you—but SCHLITZ, with SUNSHINE Vitamin D, is extra good for you. Drink it daily—for health with enjoyment.” If it sounds antiquated, think about that in 2022 beer model Corona launched Corona Sunbrew, a nonalcoholic beer fortified with vitamin D.
Beer is just not, nevertheless, a well being meals. The “natural, evolutionarily appropriate way to get vitamin D is through synthesis in your skin,” says Anastassios Pittas, chief of the division of endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism at Tufts Medical Center. But that doesn’t require getting a sunburn. It seems that you do not want excessive doses of solar to get adequate vitamin D. A 2010 research calculated that between April and October, somebody in Boston with 25 p.c of their pores and skin uncovered would wish between three and eight minutes of daylight per day to get sufficient. Of course, within the winter it is perhaps difficult to search out even this quantity of solar at some latitudes.
Fortunately, your physique is supplied to cope with this type of variation. Your liver and fats cells retailer vitamin D for future use, Pittas says. That means you do not essentially want a giant dose day by day. Your vitamin D cache usually lasts for about 10 to 12 weeks, so even when you do not have a whole lot of day by day D coming in through sunshine within the winter, Pittas says, you can nonetheless have sufficient circulating out of your liver to keep up sufficient calcium and phosphorus ranges. It’s pure to have a winter dip, he says, however that’s worrisome provided that you are already operating low on vitamin D.
Interest in getting further vitamin D took off when research instructed it’d decrease the chance of coronary heart illness, most cancers, diabetes, and a spread of different circumstances.
The drawback is that this proof got here principally from observational research, a sort of research that may’t present trigger and impact and that may produce deceptive outcomes, Manson says. These observational research appeared for associations between vitamin D ranges and a specific well being situation or in contrast vitamin D standing amongst individuals with a situation and people with out. For occasion, an offshoot of the Framingham Heart Study revealed in 2008 adopted greater than 1,700 individuals with out prior heart problems over about 5 years and located that folks with low vitamin D ranges had the next danger of growing coronary heart illness. The outcomes generated a whole lot of pleasure and hype round vitamin D, Manson says.
Diabetes, too, appeared to trace with D ranges. A research revealed in 2010 adopted shut to six,100 individuals in Tromsø, Norway, over a interval of 11 years. Their incidence of sort 2 diabetes confirmed an inverse relation with blood ranges of vitamin D earlier than their physique mass was taken under consideration: larger D ranges had been correlated with fewer instances of diabetes. Similarly, a 2011 research of greater than 6,500 individuals in Australia discovered that the chance of growing diabetes over the course of 5 years was lowest for the individuals with the best D ranges.
All these observational research have a basic weak spot: they’ll establish a co-occurrence between vitamin D and a illness, however they cannot show there’s a cause-and-effect relation—or, if there’s one, they cannot establish by which path it’d go. Think of it this manner: there is a sturdy hyperlink between somebody’s wealth and the value of their automotive, however that does not imply shopping for an costly automobile will make you wealthy.
“Just because you see an association, that doesn’t mean that, okay, if we fix the serum vitamin D level, that’s going to fix the problem,” says doctor Leila Kahwati, affiliate director of the Research Triangle Institute–University of North Carolina Evidence-based Practice Center. There is perhaps different elements at play. For occasion, individuals who take vitamin D dietary supplements could also be extra well being aware and do different issues that defend them from illness, and people who find themselves already ill most likely spend much less time outside getting vitamin D from daylight.
For these causes, randomized managed trials, by which researchers recruit a gaggle of individuals after which assign them to obtain totally different therapies (or a placebo), are thought-about the strongest type of medical proof, says doctor Jodi Segal, affiliate director of the Center for Health Services and Outcomes Research at Johns Hopkins University’s college of public well being. A randomized design makes it more likely that any variations between the research and placebo teams are attributable to the intervention quite than by another variable.
In 2009 Manson and her crew launched into the world’s largest and most far-reaching randomized vitamin D trial, referred to as VITAL. The research adopted practically 26,000 usually wholesome adults, randomized to obtain both 2,000 worldwide items (IU) of vitamin D or a placebo, for a mean of 5.3 years. The volunteers had been virtually evenly cut up between women and men, and 20 p.c of the individuals had been Black. The research was designed to take a look at whether or not vitamin D dietary supplements may stop most cancers or heart problems.
The outcomes got here as a shock. Not solely did vitamin D not make a dent in charges of most cancers or coronary heart illness, however the trial additionally discovered that vitamin D didn’t stop falls, enhance cognitive perform, cut back atrial fibrillation, change physique composition, cut back migraine frequency, enhance stroke outcomes, lower age-related macular degeneration, cut back knee ache and even cut back the chance of bone fractures. The discovering about fractures “was a real surprise to many people,” Manson says.
Extra vitamin D additionally did not decrease diabetes danger. In a trial revealed in 2019 within the New England Journal of Medicine, Pittas and his colleagues randomized greater than 2,400 individuals in danger for diabetes to take both 4,000 IU of vitamin D or a placebo day by day. After two and a half years, an analogous variety of individuals in every group went on to develop the illness.
The Vitamin D Assessment Study (ViDA) recruited 5,110 volunteers ages 50 to 84 in New Zealand and randomized them to get both a placebo or 200,000 IU of vitamin D per thirty days—an enormous dose a lot larger than the really useful day by day allowance. The research discovered that ranges made no distinction in heart problems, acute respiratory infections, nonspinal fractures, falls and all sorts of most cancers. Other trials discovered that vitamin D supplementation didn’t cut back mortality charges or the chance of invasive most cancers. These outcomes, together with others popping out of VITAL, led to rising skepticism about vitamin D by round 2020, says Clifford Rosen, an endocrinologist on the Maine Medicine Center’s Research Institute.
The ViDA trial did discover some modest complement advantages in individuals who had began the research with a vitamin D deficiency. But what precisely does “deficiency” imply?
It doesn’t imply what many docs suppose it does, apparently. The widespread notion that a lot of America is strolling round poor in vitamin D got here from what Manson calls a “misinterpretation and misapplication” of the traditional ranges for vitamin D set by the Institute of Medicine (IOM, now often called the National Academy of Medicine) greater than a decade in the past.
Here’s what occurred. In 2011 the IOM convened an skilled committee to conduct a radical evaluation of all present research on vitamin D and well being. Based on this proof, the committee concluded that the bone-strengthening advantages of vitamin D plateau when blood ranges (as measured by an ordinary vitamin D blood take a look at) attain 12 to 16 nanograms per milliliter. They additionally discovered that there have been no advantages to having ranges above 20 ng/ml. So they set that because the ceiling for his or her suggestions whereas noting that almost all of the inhabitants is simply fantastic at 16 ng/ml.
According to measurements of vitamin D ranges within the normal U.S. inhabitants collected by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, most individuals had ranges of 20 ng/ml or extra in 2011. Levels have really risen since then, which means that most individuals are properly throughout the medical suggestions, says Rosen, who served on the IOM committee.
So the place did the concept of mass deficiency come from? First off, 20 ng/ml was erroneously interpreted by some health-care staff because the naked minimal, as a substitute of a degree marking good quantities for most individuals. Recall the IOM discovered that 16 ng/ml was passable. The implication of the misreading was that folks wanted greater than 20 ng/ml for good bone well being, Manson says.
But a few of the confusion stems from a second set of tips that one other medical group, the Endocrine Society, put out across the identical time because the IOM requirements. Whereas the institute made suggestions for wholesome populations, the society’s tips had been aimed toward clinicians, notably these caring for sufferers in danger for vitamin D deficiency. The makers of those tips checked out a lot of the identical proof that the institute committee reviewed, however they concluded that something below 20 ng/ml represented “deficiency,” and so they labeled vitamin D ranges of 21 to 29 ng/ml as one thing they referred to as “insufficiency.”
The phrases “insufficiency” and “deficiency” have created “a tremendous amount of confusion,” says Christopher McCartney, an endocrinologist and medical analysis specialist on the University of Virginia School of Medicine. He provides that the Endocrine Society tips have been largely taken to imply that everybody wants vitamin D ranges of 30 ng/ml or extra.
The IOM tips do not help that conclusion, and in 2012 the institute committee revealed a rebuttal paper, “IOM Committee Members Respond to Endocrine Society Vitamin D Guideline.” It contended that points of the society’s tips, together with the definition of insufficiency, weren’t properly supported by proof. For occasion, the society’s tips used a 2003 research of solely 34 individuals to help its rivalry that vitamin D ranges above 30 ng/ml are higher for calcium absorption. At the identical time the society’s committee ignored a research of greater than 300 folks that discovered that calcium absorption just about maxes out at vitamin D ranges of 8 ng/ml.
Michael Holick was the lead creator of the Endocrine Society tips. An endocrinologist at Boston University’s medical college, Holick says that the insufficiency customary is justified by an observational study from 2010. It discovered that a few quarter of the in any other case wholesome grownup males had proof of osteomalacia, a bone-softening situation linked to low vitamin D ranges. The research did not discover bone issues in individuals above 30 ng/ml; therefore Holick’s rivalry that 30 was the minimal.
The Endocrine Society is at the moment within the strategy of updating its tips, with McCartney serving as its methodologist. He says that the brand new tips will give attention to randomized trials, not observational ones, and so they’ll watch out to name out the proof gaps that stay.
The committee can be taking care to keep away from outdoors affect. “Our conflict-of-interest policy is much more transparent and rigorous than I think it has been in the past,” McCartney says. Holick, who ran the unique guideline-writing group, advocates giant doses of vitamin D dietary supplements. Although there isn’t a proof that his judgments had been affected by industrial ties, Holick has obtained no less than $100,000 from numerous corporations concerned in making vitamin D dietary supplements and assessments, in accordance with a 2018 investigation by Kaiser Health News (now KFF Health News) and the New York Times. McCartney says that, partially, considerations raised about Holick prompted the Endocrine Society to pay further consideration to ethics.
Holick made a reputation for himself espousing the health-promoting powers of vitamin D and wrote a e-book referred to as The Vitamin D Solution: A 3-Step Strategy to Cure Our Most Common Health Problems. He takes 6,000 IU day by day and advises his sufferers to take a minimal of two,000 to three,000 IU per day. For comparability, the 2011 IOM report calculated that the common individual’s day by day requirement is 400 IU.
Holick advised Scientific American that it’s “not true” that he has conflicts of curiosity. He acknowledged receiving trade cash however mentioned many of the cash had “nothing to do with vitamin D” and was as a substitute “associated with me talking about a new drug coming on the market,” for sufferers with power hypoparathyroidism.
Still, some within the discipline see Holick’s evangelism for vitamin D as conflicting along with his position engaged on the Endocrine Society tips. Rosen says that the rules “were driven by Mike. He was the chair of the committee.” Rosen skilled with Holick and considers him a good friend. “He’s a good guy,” Rosen says. But “just because you hypothesize something doesn’t mean you have to stick with it…. Michael went to extremes to show that vitamin D had something to do with chronic diseases.”
Much of the knowledge put out by corporations providing direct-to-consumer testing nonetheless claims that something below 30 ng/ml is low. Athlete Blood Test, for example, markets blood assessments to energetic individuals and encourages them to intention for a degree of no less than 50 ng/ml. While engaged on this story, I had my vitamin D checked by one other testing firm, and the laboratory outcomes got here again with reference ranges of 30 to 100 ng/ml, implying that something below 30 was not sufficient. The lab clarification did word that the IOM’s cutoff was 20. (My quantity was 32.8 ng/ml, which means that sunshine actually can assist—I by no means take dietary supplements, however I train day by day outside.)
More than 10 million vitamin D assessments are carried out yearly within the U.S., although these assessments will not be really useful by main medical organizations such because the Endocrine Society, the National Academy of Medicine and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Three medical societies have endorsed a suggestion to “not order population-based screening for vitamin D” from Choosing Wisely, an initiative to scale back wasteful medical practices.
Yet the testing goes on. A research revealed in 2020 examined medical information from a big regional well being system in Virginia and located that about 10 p.c of the system’s sufferers had been examined for D ranges, though lots of the assessments weren’t indicated by the sufferers’ well being circumstances. Supporting the concept of the assessments being unneeded, 75 p.c of the outcomes got here again as regular, says research creator Michelle Rockwell, an assistant professor of household and group drugs on the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University. Furthermore, a few of the take a look at outcomes categorized as irregular could have been thought-about simply fantastic by the IOM requirements; the research used the next reference vary of 30 to 99.9 ng/ml.
Given the VITAL trial’s giant dimension and extensive scope, many vitamin D researchers hoped it might put lots of the purported advantages of vitamin D dietary supplements to relaxation. “But there’s a religiosity around vitamin D,” Rosen says. Rosen wrote an editorial within the New England Journal of Medicine saying most individuals can cease taking vitamin D dietary supplements and that the big VITAL research was a “decisive verdict.” Even then, he says, he bought pushback from colleagues who refused to consider that vitamin D wasn’t the panacea they’d come to consider. “The evidence is out there,” he says. “People don’t want to pay attention to it.”
Although most individuals do not want dietary supplements, there are exceptions. Breast milk doesn’t include sufficient vitamin D for infants, so the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that infants who’re breastfed (partially or solely) be supplemented with 400 IU a day of vitamin D starting within the first few days of life to advertise stronger bones. In addition, the academy says all infants and youngsters who eat lower than 32 ounces of vitamin D–fortified components or milk per day must also get dietary supplements of 400 IU. Crohn’s illness, cystic fibrosis, celiac illness, and sure liver and kidney circumstances could cause vitamin D deficiency, so individuals with these sicknesses may also want dietary supplements. People who’re hospitalized or who’ve had gastric bypass surgical procedure may additionally turn out to be poor.
Typical assessments could, nevertheless, overestimate vitamin D issues in some individuals of African ancestry. The customary take a look at measures circulating blood ranges of a vitamin D precursor, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, that’s certain to a specific protein. A 2013 New England Journal of Medicine research discovered that some individuals have gene variants that permit circulation of extra of the unbound precursor kind and fewer of the certain one. So by specializing in the certain model, the take a look at underestimates whole vitamin D availability. The research, which concerned greater than 2,000 individuals, discovered that those that had been Black had decrease vitamin D ranges than white individuals in accordance with the usual blood take a look at. Yet these Black individuals had sturdy bones and good calcium ranges.
Manson is fast to warning that extra is not essentially higher with regards to vitamin D. “Vitamin D is essential to good health, but we require only small to moderate amounts,” she says. She would not dissuade individuals from taking dietary supplements of as much as 2,000 IU per day, however she would not suggest larger ranges as a result of some research have discovered that extra vitamin D can improve the chance of harmful falls—researchers speculate that intermittent excessive doses have an effect on the central nervous system, which may impair stability. And whether or not you are taking dietary supplements or not, you’re most likely getting supplemental vitamin D in case you eat dairy merchandise, breakfast cereal, plant milks, or different fortified meals, says Price, creator of Vitamania.

Despite the disappointing trials on vitamin D, it isn’t time to dismiss the vitamin fully, Manson says. There’s nonetheless lots extra to grasp. For occasion, the VITAL trial confirmed that amongst slender or normal-weight individuals, outlined as having physique mass indexes of 25 or much less, vitamin D dietary supplements appeared to decrease the incidence of most cancers, most cancers deaths and autoimmune illness. This protecting impact didn’t present up amongst heavier individuals with larger physique plenty. Manson cautions that these numbers must be verified by additional work as a result of they’re from a smaller subanalysis of the primary research. But it is attainable that extra physique fats could by some means hamper the effectiveness of vitamin D. Obesity itself is a danger issue for each most cancers and autoimmune illness, so it is doubtless that any connection is complicated.
Pittas stays satisfied that for individuals at excessive danger for diabetes, vitamin D can play a task in prevention. His earlier trial did trace that individuals who obtained supplemental vitamin D had been much less more likely to develop diabetes: 24.4 p.c of them bought the illness, versus 26.9 p.c of the placebo group. That distinction alone was too small to be statistically vital. But when he pooled the outcomes with these of two different randomized trials, he discovered a modest however constant good thing about a few 3 p.c discount in diabetes danger over three years.
There are some constructive indicators for treating COVID, too. Clinical and lab research have proven that vitamin D has a constructive impact on the immune system and may tamp down irritation. “We saw this in our VITAL trial,” Manson says. Holick provides that vitamin D can assist downregulate so-called cytokine storms, immune system overreactions which have provoked life-threatening respiratory issues in some COVID sufferers.
Manson’s analysis group has two randomized trials at the moment underway to check whether or not vitamin D can assist with COVID. One is investigating whether or not high-dose vitamin D can cut back the possibilities of getting the extended and debilitating ailment of long COVID. The different trial is whether or not 1,000 IU of vitamin D per day can cut back the chance of that sickness or total symptom severity. Manson hopes to complete analyzing the information in 2024.
Vitamins maintain a sure attract. They’re low-cost, they’re comparatively protected, and there is a sense, emphasised by entrepreneurs, that they are “natural” and subsequently by some means higher than medicine, Rosen says. “There’s this magical thinking that vitamins improve health, and some people do feel better” when taking them, he says, pointing to the placebo impact as a possible contributor.
The ups and downs of vitamin D provide a lesson in humility. The relation between the vitamin and illness is much extra difficult and nuanced than it first appeared and a reminder that scientific understanding is at all times evolving.
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link