
[ad_1]
FP TrendingSep 21, 2020 17:16:39 IST
Scientists have got their hands on the most detailed global infrared views ever produced of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. These composite images were made from the data received by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft.
According to the latest pictures, researchers have found concrete evidence of fresh ice to have been deposited on the surface of Enceladus.
It was in 2005 that scientists found that the moon had giant occasional bursts of ice grains and vapour originating from an ocean that lay under its icy crust. This was also known because of the Cassini spacecraft.
Managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, ESA (the European Space Agency) and the Italian Space Agency.
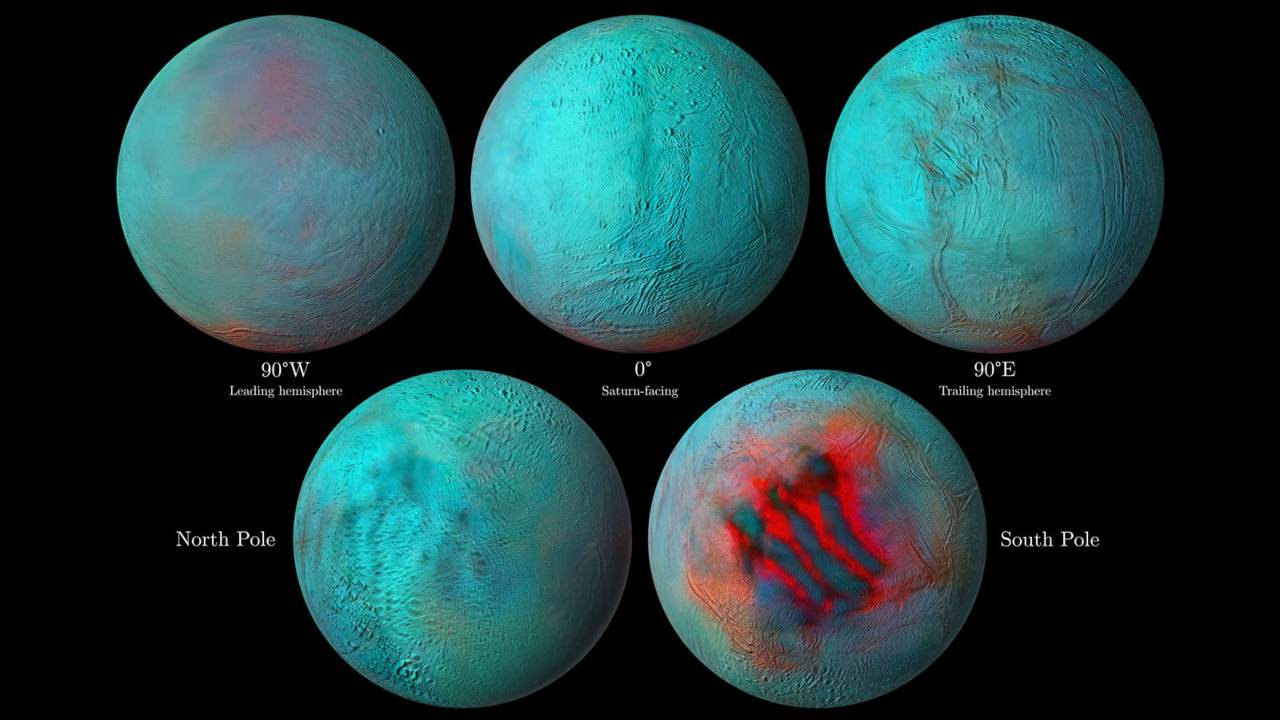
Detailed infrared images of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, with reddish areas indicating fresh ice that has been deposited on the surface. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/LPG/CNRS/University of Nantes/Space Science Institute
The craft had a Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS) that collected light reflected off the surface of Saturn, its rings and its ten major icy moons. As the instrument captured lights in different wavelengths, it then separated them to give more information about the material that was reflecting the light.
Thereafter, in a bid to map the moon, data from the VIMS was combined with detailed images captured by Cassini’s Imaging Science Subsystem (ISS) to make composite images.
The recent images reveal that a geologic activity like resurfacing of the landscape has occurred in both the hemispheres of Enceladus. While it was known that the South Pole is young, some fresh ice has been churning out in the North Pole as well.
Gabriel Tobie, VIMS scientist with the University of Nantes in France and co-author of the latest study said, “The infrared shows us that the surface of the South Pole is young, which is not a surprise because we knew about the jets that blast icy material there”.
Further, the infrared images prove that “one large region in the Northern Hemisphere” was also apparently young and “probably active not that long ago, in geologic timelines”.
The study is accessible from the journal Icarus.
[ad_2]
Source link