
[ad_1]
A evaluate article printed within the journal Antioxidants supplies an in depth overview of nanoparticle-based methods to enhance the bioavailability and bioactivity of curcumin.
 Study: Enhancing the Bioavailability and Bioactivity of Curcumin for Disease Prevention and Treatment. Image Credit: Microgen / Shutterstock
Study: Enhancing the Bioavailability and Bioactivity of Curcumin for Disease Prevention and Treatment. Image Credit: Microgen / Shutterstock
Background
Curcumin, turmeric’s fundamental bioactive compound, is a polyphenol present in Curcuma longa roots. This compound has quite a few well being advantages, together with anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-microbial, wound-healing, and lipid-lowering properties.
Curcumin has low bioavailability in human organs and is quickly transformed to numerous bioactive metabolites after intestinal absorption. Dried turmeric powder ready from Curcuma longa roots incorporates about 2-5% of curcumin.
Curcumin consumed by dietary sources is adequate to influence the intestine microbiota. However, because of fast metabolism, the focus of intact curcumin within the circulation turns into very low (sub-micromolar concentrations), which is inadequate to set off mobile signaling and gene expression, as noticed in in vitro research with cultured cells.
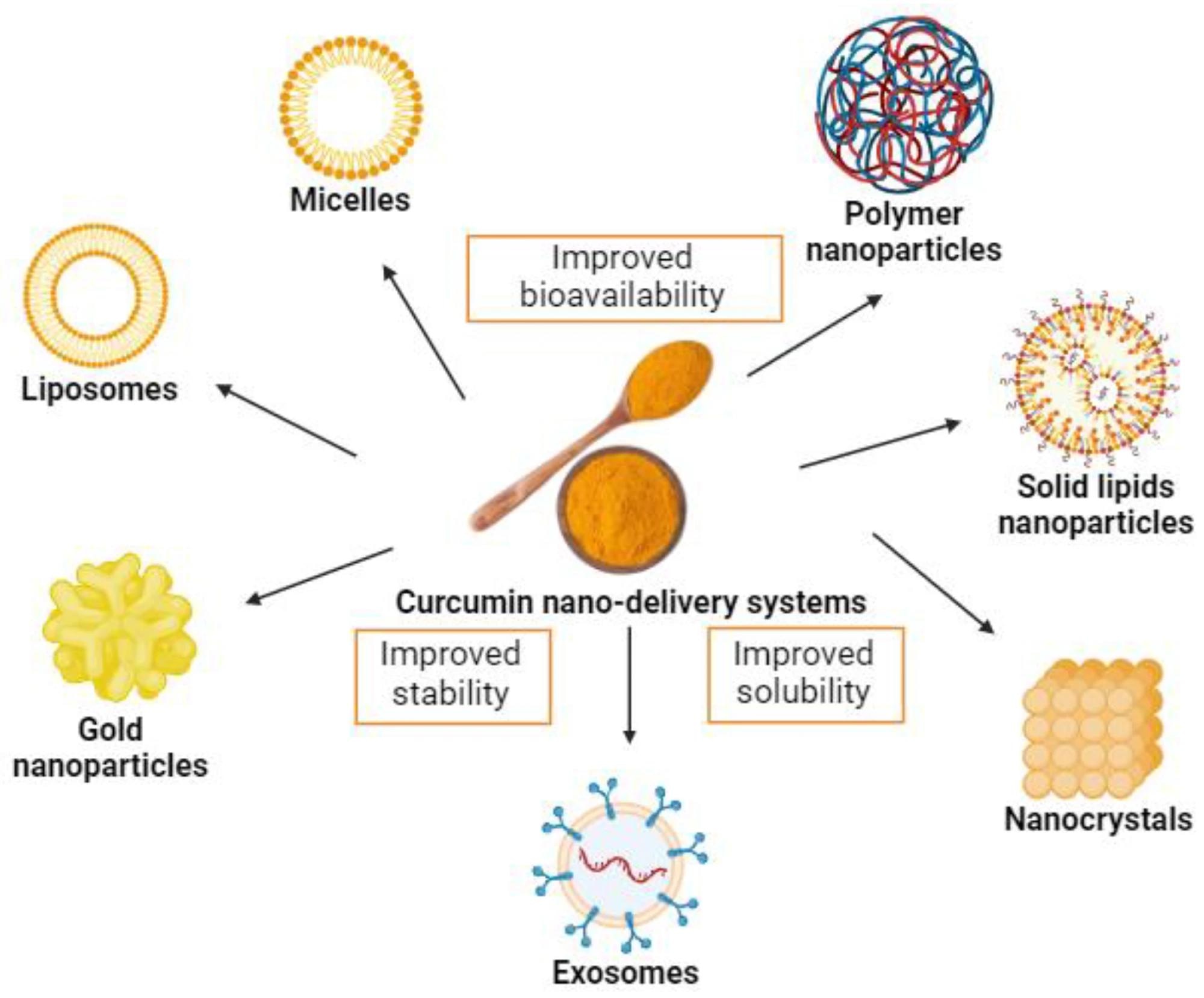 Examples of curcumin nano-delivery programs.
Examples of curcumin nano-delivery programs.
Strategies to extend curcumin bioavailability
Dietary curcumin is inefficiently absorbed throughout the intestinal epithelium and undergoes fast metabolism and systemic elimination. In an aqueous resolution with a impartial pH, the enol state of curcumin is fashioned, which reduces the steadiness of curcumin.
Several nanoformulations have been developed to extend curcumin focus within the circulation in addition to in particular cells, tissues, and organelles. These nanoformulations have been designed to extend curcumin solubility, enhance stability throughout gastrointestinal absorption, alter absorption routes, and inhibit detoxing enzymes utilizing adjuvants.
The newest era of curcumin nanoformulations can enhance free curcumin bioavailability in plasma by greater than 100-fold and enhance absorption, mobile uptake, permeability by the blood-brain barrier, and tissue distribution.
Factors that enhance curcumin bioavailability embody composition, dimension, and route of administration of nanoparticles. Curcumin preparations with smaller-size nanoparticles have been discovered to extend bioavailability when administered orally. In distinction, larger-size nanoparticles have been discovered to extend bioavailability when administered intravenously.
Curcumin nanoformulations can induce senescence in malignant and regular cells, thus successfully treating numerous most cancers varieties and age-related illnesses, together with cardiometabolic illnesses, neurodegenerative illnesses, and liver, lung, and gastrointestinal illnesses.
Regarding mode of motion, current proof signifies that curcumin acts as an antioxidant and anti inflammatory compound to cut back the manufacturing of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and modulate mobile signaling and gene expression associated to inflammatory pathways. These actions work synergistically to take care of homeostasis of mobile macromolecules (proteins, DNA, and lipids).
These actions may be elevated by incorporating curcumin in nanoparticle-based formulations, equivalent to polymeric curcumin–bioperine–PLGA. The isomerization of curcumin to cis-trans curcumin is thought to extend its potential to bind adenosine receptors. Incorporation of cis-trans curcumin into nanoformulations is taken into account to be a useful technique to extend its therapeutic efficacy towards inflammatory illnesses.
Regarding security profile, current scientific trials point out that almost all of curcumin nanoformulations are well-tolerated and protected to be used in people.
Anti-microbial actions
Curcumin is thought to exert an anti-microbial impact towards each Gram-positive and Gram-negative micro organism, and this exercise is helpful for topical purposes towards pores and skin an infection and oral and intestinal purposes. Moreover, curcumin can not directly forestall an infection by inhibiting bacterial development in meals.
The anti-microbial actions of curcumin may be enhanced by incorporating it into nanoformulations. Administration of curcumin with different compounds, equivalent to antibiotics, honey, or different polyphenols, also can enhance its anti-microbial and biofilm inhibitory actions.
Effects of curcumin nanoformulations within the gastrointestinal tract
Several nanotechnology-based programs, equivalent to micelles, liposomes, exosomes, phospholipid complexes, nanoemulsions, nanostructured lipid carriers, and biopolymer nanoparticles, have been discovered to extend oral curcumin bioavailability.
Nanoparticle curcumin known as ‘Theracurmin’ has been discovered to suppress colitis in mice by modulating intestine microbiota. Improvement in intestine microbiota composition has additionally been achieved utilizing nanobubble curcumin extract. Curcumin loaded with nanostructured lipid carriers has been discovered to cut back colonic irritation in animals.
The incorporation of curcumin in liposomes has been discovered to extend its anticancer exercise by enhancing gastrointestinal absorption. Moreover, the administration of curcumin with different bioactive compounds, equivalent to piperine and salsalate, has been discovered to extend curcumin bioavailability and bioactivity.
Effects of curcumin nanoformulations in liver and adipose tissue
Curcumin nanoformulations with adjuvants, equivalent to piperine and quercetin, have been discovered to extend its bioavailability and bioactivity considerably. Various nanotechnology-based supply programs, equivalent to micelles, liposomes, polymeric, metallic, and strong lipid nanoparticles, have been discovered to extend curcumin bioavailability.
The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic properties of curcumin make it a possible therapeutic compound for liver illnesses. In liver illnesses, curcumin nanoformulations have been discovered to extend its therapeutic efficacy by growing curcumin solubility, bioavailability, and membrane permeability and enhancing its pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and biodistribution.
Effects of curcumin nanoformulations on the cardiovascular system
Curcumin encapsulated in carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles conjugated to a myocyte-specific homing peptide has been discovered to extend the cardiac bioavailability of curcumin. The formulation has additionally been discovered to enhance cardiac perform by lowering the expression of hypertrophy marker genes and apoptotic mediators.
Several curcumin nanoformulations, equivalent to hyaluronic acid-based nanocapsules, nanoparticles encapsulated in PLGA or nanoemulsion programs, have been discovered to extend the aqueous solubility of curcumin and subsequently forestall hypertension in animals. Similar cardio-protective results have been noticed utilizing nanocurcumin polymer-based nanoparticles and curcumin and nisin-based polylactic acid nanoparticles. These formulations have been discovered to forestall myocardial injury and enhance cardiac muscle capabilities.
Effects of curcumin nanoformulations on the mind
Curcumin complexed with galactomannans has been discovered to have higher blood-brain barrier permeability and better efficacy in stopping neuroinflammation, anxiousness, fatigue, and reminiscence loss in each people and animals.
Curcumin-laden liposomes have been discovered to exert anti-amyloidogenic and anti inflammatory results in animal and mobile fashions of Alzheimer’s illness. Curcumin’s preventive actions towards Alzheimer’s illness are related to its potential to cut back amyloid-beta manufacturing and tau aggregation, that are main hallmarks of Alzheimer’s illness.
However, scientific trials involving sufferers with gentle to average Alzheimer’s illness couldn’t discover any helpful impact of curcumin in lowering illness biomarkers and enhancing cognitive capabilities.
A current scientific trial involving non-demented adults, alternatively, has proven that oral curcumin therapy can enhance reminiscence and cut back amyloid and tau accumulation within the amygdala and hypothalamus.
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link