[ad_1]
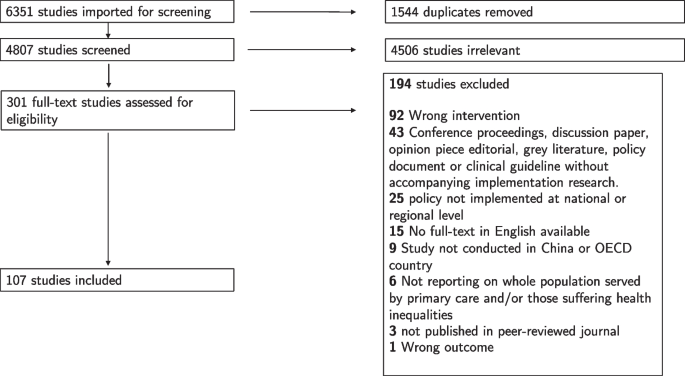
A complete of 6351 information had been recognized by the search technique of which 1544 had been duplicates. Following title and summary screening, 301 articles underwent full-text screening with 107 articles included (Fig. 1) [6,7,8, 17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120].
Fifty-four per cent of the included research employed quantitative strategies alone, 28% qualitative strategies alone, and 14% blended strategies, and 4% had been evaluations of the literature. Included research had been performed in 14 of 39 OECD plus China, with six international locations (the USA, China, Canada, the UK, Australia, and Sweden) accounting for over 80% of research (Additional file 1: Fig. S1). Two research examined PCT throughout a number of jurisdictions in Australia, Canada, and the USA [27, 28]. Characteristics of all included research are proven in Additional file 1: Table S3 [6,7,8, 17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120].
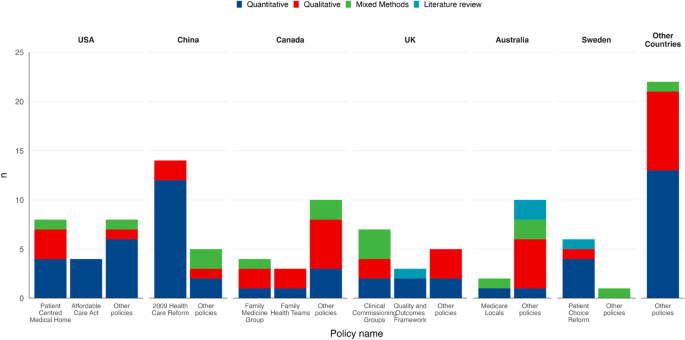
Figure 2 reveals the particular PCT insurance policies evaluated in included research for the six international locations contributing 80% of the included research and the remaining 9 international locations aggregated. The most ceaselessly studied insurance policies had been the 2009 Health Care Reform in China (n = 14), the Patient-centred medical residence (PCMH) within the USA (n = 8), and the Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCGs) within the UK (particularly, England) (n = 7). Slightly over half of the research (n = 59 [55%]) evaluated the insurance policies that had been unnamed or appeared solely as soon as.
The most ceaselessly described elements of PCT had been growth of the MDT (n = 49 [46%]), various fee mechanisms (n = 45 [42%]), and elevated entry to major care (n = 40 [37%]) (Table 1 and Additional file 1: Fig. S2). Almost all PCT insurance policies included a number of elements. For instance, 21 research (42%) together with an growth of MDT element additionally included various fee mechanisms and/or elevated major care entry. The 2009 Health Care Reform in China accounted for 22% of research describing various fee mechanisms and 33% of research describing elevated major care entry. Otherwise, described elements of PCT had been distributed throughout international locations and insurance policies (Additional file 1: Figs. S2 and S3).
Of the 20 research performed within the USA [27, 28, 103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120], eight evaluated PCMH with PCT elements together with growth of the MDT, high quality enchancment, and knowledge know-how (Table 1) [27, 103, 107, 108, 115, 117,118,119]; 4 evaluated the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which primarily aimed to extend major care entry [109, 113, 114, 116]; and the remaining eight evaluating different insurance policies not replicated in different research. The majority (14/19) of research performed in China evaluated the 2009 Health Care Reform and related insurance policies together with the National Essential Medicines Policy and the New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme [41, 43,44,45, 47,48,49,50,51,52,53, 56, 57, 111]. Components of this reform included elevated major care entry, various fee mechanisms, and elevated monetary assets (Table 1). Four Canadian research explicitly recognized Family Medicine Groups (FMGs) incorporating a variety of PCT elements (Table 1) [27, 30, 34, 40]. Family Health Teams (FHTs) had been talked about in three research [8, 32, 38] together with analysis of MDT growth and various fee mechanisms. Notably, 5 research performed in Canada had been assessment papers both incorporating a literature assessment or professional views [7, 8, 27, 28, 39]. Of the 15 UK papers, seven [90, 91, 94, 97, 99,100,101] evaluated CCGs with PCT elements together with change of governance and various fee mechanisms. Three research [88, 89, 102] evaluated the Quality & Outcomes Framework (QOF) which included various fee mechanism and monetary incentives. Half of papers together with analysis of Australian PCT didn’t title a particular coverage [19,20,21,22, 25, 26]. These papers aimed to provide an summary over a time period or determine boundaries and facilitators to implementation. Six of seven research performed in Sweden evaluated the Primary Health Care Choice Reform which concerned an elevated involvement of the personal and/or third sector within the provision of major care [6, 77,78,79,80,81].
A variety of consequence measures had been examined within the included research (Table 2 and Additional file 1: Fig. S4). The most ceaselessly used had been views of GPs (n = 29 [27%]), views of managers (n = 29 [27%]), or views of different MDT members (n = 25 [23%]). These research predominantly employed qualitative or blended technique methodologies (Additional file 1: Fig. S5). Twenty-nine research (27%) used an consequence distinctive to that examine or utilized in just one different included examine. Examples embrace medicine use [44, 48], continuity of care [92], and self-assessed well being [49]. Fifteen research (14%) measured affected person views, and 6 (5%) measured affected person satisfaction. The most ceaselessly employed outcomes in quantitative research had been distinctive to that examine or analysed the impact of PCT on well being care use (Table 2, Additional file 1: Figs. S4 and S5).
Twenty-seven of 29 research [19, 21, 23, 24, 34, 37, 38, 40, 57, 58, 61,62,63,64,65, 71, 81, 86, 87, 90, 95,96,97,98, 101, 117,118,119,120] together with GP views as an consequence additionally measured both managerial views (23 research), different MDT views (23 research), or affected person views (5 research). Three research evaluated the points of the PCMH within the USA and located difficulties in recruiting MDT members [118], anticipated employees satisfaction [117], and recognized vital coaching to help with PCMH implementation (Table 2) [119]. One examine discovered low satisfaction amongst GPs following the 2009 Healthcare Reform in China [57]. Two research together with GP views in Canada reported detrimental results following implementation of FMGs [34, 40]. In the UK, three research included the views of GPs on CCGs and located issues about outsourcing help capabilities on account of potential lack of data or funding [90, 97, 101].
Six research measured affected person satisfaction. All reported enhancements in satisfaction following reforms in China [50, 54], the Netherlands [68], Turkey [83, 84], and Sweden [79]. Qualitative research together with affected person views didn’t report patient-specific outcomes however focussed on employees efficiency or well being care supply findings [56, 63, 64, 86, 96]. One exception was present in Portugal the place blended outcomes by way of affected person views in direction of implementation of major well being care reform had been reported [76]. Other quantitative research discovered optimistic affected person perceptions of change following the introduction of the ACA within the USA [113] and detrimental views of a voucher scheme launched in Hong Kong [42]. One UK examine discovered that bigger observe measurement could also be related to poorer continuity of care and that collaborative working amongst practices had no impact on affected person expertise [93].
Nineteen research included measurement of major or secondary well being care use [30, 33, 43, 51, 53, 55, 66, 69, 73, 79, 80, 83, 91, 92, 105, 107, 110, 116, 120]. Only considered one of these (performed in IL, USA) reported a optimistic advantage of PCT of diminished secondary care use [105]. One examine [107] evaluating PCMH within the USA discovered an affiliation with diminished hospitalisations, regardless of increased emergency division use. Another examine evaluating the ACA discovered no change in preventable hospitalisations [116]. Five research evaluating the 2009 Health Care Reform in China [41, 43, 47, 51, 53] discovered a desired enhance in major care use but additionally elevated secondary care use, significantly in rural areas, reductions in out-of-pocket expenditure for outpatients though not inpatients, and excessive ranges of inappropriate hospital use. One examine evaluating FMGs in Canada discovered no enchancment in fairness of entry to major care or secondary care use [30]. In the UK, one examine famous the implementation of CCGs didn’t end in diminished hospitalisations and, perversely, famous elevated GP-referred specialist clinic visits [91].
Thirty-seven research (35%) evaluated PCT within the context of ageing populations or well being inequalities though solely three particularly evaluated the previous (Additional file 1: Fig. S6). Twenty reported on outcomes of PCT for these residing in disadvantaged areas [6, 21, 24, 25, 30, 31, 48, 49, 52, 63, 69, 77, 78, 83, 88, 95, 102, 110, 116, 117]. Three of those [48, 49, 52], reporting on the Chinese 2009 Health Care Reform, confirmed elevated major care entry, significantly in low-income areas, and elevated demand for companies. One [49] reported an enchancment in well being fairness; nonetheless, one other [48] famous that out-of-pocket expenditure rose. Seventeen different research performed in Australia, Canada, Ireland, New Zealand, Sweden, Turkey, the UK, and the USA reported ambiguous outcomes or worsening well being inequalities for disadvantaged populations [63].
The three research evaluating PCT within the context of older folks reported excessive ranges of satisfaction with a brand new administration pathway for older folks in southwest China [54], detrimental outcomes (together with worse continuity-of-care) following the introduction of a named GP coverage in England [92], and elevated entry favouring youthful quite than older folks from extra personal sector involvement in major care supply in Sweden [77].
Ten research evaluated PCT in mild of city/rural inequalities. Six of those had been performed in China [41, 43, 45, 55, 56, 111]: two reported optimistic outcomes significantly elevated major care entry in rural areas [41, 43]; three reported detrimental outcomes, together with poor GP satisfaction [45], a ‘brain-drain’ of medical doctors from rural to city areas [49], and variations between provinces resulting in regional disparity [111]. A newer examine in China reported blended outcomes [55]. Elsewhere, one examine evaluating expanded major care in Turkey [83] reported improved entry, satisfaction, and repair high quality in rural areas. Studies in Portugal [75] and Australia [20] highlighted the problem within the implementation of centrally designed PCT insurance policies in geographically dispersed populations. One UK examine discovered a non-significant impact of QOF on mortality in city or rural areas [88].
Thirteen research evaluating PCT implementation within the context of ethnic minorities had been performed in Australia [20, 23,24,25,26], New Zealand [69, 70], the UK [88, 102], the USA [114, 117], Canada [36], and Sweden [82]. Positive outcomes for ethnic minorities, together with elevated entry and quality-of-care, had been reported in three research [23, 70, 82], while six research reported detrimental, blended, or equivocal outcomes [24, 25, 69, 88, 102, 114]. The remaining research targeted on service, quite than affected person outcomes [20, 26, 36, 117].
Forty-one research (38%) explicitly recognized boundaries or facilitators to PCT implementation, of which 59% had been performed in Canada, Australia, or the USA. The majority had been qualitative or blended technique research (Additional file 1: Fig. S7). Thematic evaluation of those research recognized 4 foremost themes: (a) management, coverage, and communication; (b) change, tradition, and relationships; (c) assets and capability; and (d) targets, outcomes, and measurement (Table 3).
In the management, coverage, and communication theme, 12 research famous the significance of management in PCT implementation [27, 34, 39, 58, 63,64,65,66, 81, 101, 117, 119] which was required at increased organisational stage [58, 66, 81, 101, 119] in addition to on the stage the place companies are delivered (e.g. in GP practices) [27, 34, 63]. The significance of institutional [58, 81] and private management was highlighted, and the latter cited as a key facilitator ‘at-the-coalface’ [34, 39, 39, 63, 64]. Twelve research highlighted the significance of planning and articulation of coverage intentions to these delivering the initiative [18, 21, 36,37,38, 58, 63, 65, 72, 87, 99, 117]. This was cited as an vital aspect when there have been difficulties implementing a coverage [18, 21, 36, 58, 72, 87, 99] and likewise in optimistic examples [37, 38, 63, 65, 117]. The appropriate stability between ‘top-down’ and ‘bottom-up’ initiatives was mentioned in seven research [7, 18, 21, 27, 37, 58, 117]. Three research highlighted a scarcity of engagement the place examine members perceived ‘top-down’ PCT implementation [7, 21, 37]. However, wholly ‘bottom-up’ approaches elevated the chance of variable implementation throughout areas [18], regardless of the potential for higher engagement [117] and adaptability at a neighborhood stage [7, 27]. Two research discovered a mix of ‘top-down’ and ‘bottom-up’ approaches was more likely to yield finest outcomes [18, 58].
In the second theme of change, tradition, and relationships, reluctance or resistance to vary amongst clinicians was recognized as a barrier to PCT [21, 24, 37, 98, 101, 117]. Some research reported issues over potential reductions in major care funding [37, 101] or change in skilled roles leading to lack of expertise [98]. However, one examine famous the place perceived advantages to well being care professionals had been identified prematurely, change was not resisted [61]. Three research famous the affect of energy held by physicians and their consultant our bodies on the probability of PCT implementation [7, 40, 60]. Two research [37, 117] noticed any kind of reform includes politics and must be deliberate for on the design stage of main coverage change. The significance of private relationships between and inside totally different administrative, and/or medical ranges or in numerous jurisdictions, from central coverage improvement, by native authorities or well being authority, to direct medical care, was highlighted as important to the success or failure of PCT implementation in seven research [18, 38, 39, 51, 58, 75, 81]. There was proof of pressure between PCT insurance policies aiming to enhance inhabitants well being while major care typically prioritises power illness administration on the particular person stage [21, 24, 95]. This was significantly troublesome the place PCT concerned cross-sectoral integration or cooperation [51, 95]. Four research noticed energy struggles between GPs and different medical professionals the place roles and tasks had been altering [27, 34, 35, 61], while six cited optimistic collaboration inside groups as an vital facilitator to vary [18, 35, 37, 38, 62, 63].
The third barrier and facilitator theme was assets and capability. Nine research highlighted lack of monetary dedication as a basic barrier to PCT implementation [7, 35, 42, 51, 58, 62, 65, 72, 117] while two cited enough funding as a facilitator [36, 64]. Four research famous that point required from already very busy clinicians to adapt and implement coverage targets was typically neglected [26, 62, 63, 98], while two famous failure to account for the extra time required in geographically dispersed areas [75]. The lack of coaching was recognized as a barrier to implementation in 4 research [24, 26, 61, 119], whereas two research cited schooling and coaching as important facilitators [39]. Lastly, the availability of data know-how and technical help enabling administration and measurement was cited as a key barrier/facilitator [75, 115, 117].
In the ultimate theme of targets, outcomes, and measurement, 4 research recognized pay-for-performance incentives as a facilitator to help PCT implementation [38, 58, 66, 115]. However, three different research famous these can act as a perverse incentive; for instance, GPs being paid on a fee-for-service foundation the place wider MDT working was a coverage purpose [35, 40, 71]. Eight research reported the identification and measurement of tangible outcomes as an important facilitator of PCT [36, 51, 63, 64, 81, 94, 99, 117]. Three research indicated the significance of fine knowledge assortment and administration in an effort to allow this [20, 36, 75].
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link