
[ad_1]

IBM helps to repair evident deficiencies in its expertise system, through greater than $11 million in IT contracts it has with police. (file picture)
Photo: RNZ / Richard Tindiller
The New Zealand Police has been spending tens of millions on its principal expertise system within the face of evident deficiencies, whereas on the identical time including in high-tech data-mining instruments.
Despite an ICT evaluation two years in the past stuffed with purple flags – revealed in a brand new OIA – it has just lately added visible evaluation expertise, highly effective data-mining and new mapping to a system the place it already holds over 10 million paperwork, seven million “person identities”, and big information scrapings from the darkish internet and common web, together with folks’s social media information.
The system additionally consists of cellphone-hacking Cellebrite, amongst a protracted listing of tech capabilities most just lately up to date in April.
Police have repeatedly instructed the general public all the information it and its large tech companions collect was with good purpose, and dealt with with care.
However, IBM regarded throughout its ICT techniques two years in the past and reported again internally, within the newest evaluate obtainable from police underneath the OIA:
- “Security and compliance is sub-optimal due to lack of data classification.”
- “Critical processes do not have service to operate effectively.”
- “Confusion over who owns what data and who is responsible for ongoing data quality.”
And, worryingly for the invasive high-tech instruments carried out earlier than 2021:
- “Standards and principles are applied mainly at high-level design but are not consistently applied to detailed design.”
In truth, IBM rated eight out of 15 ICT classes as purple – “best practices do not exist with the organisation” or had solely simply been began on – six rated orange (“partially exist”), and just one inexperienced.
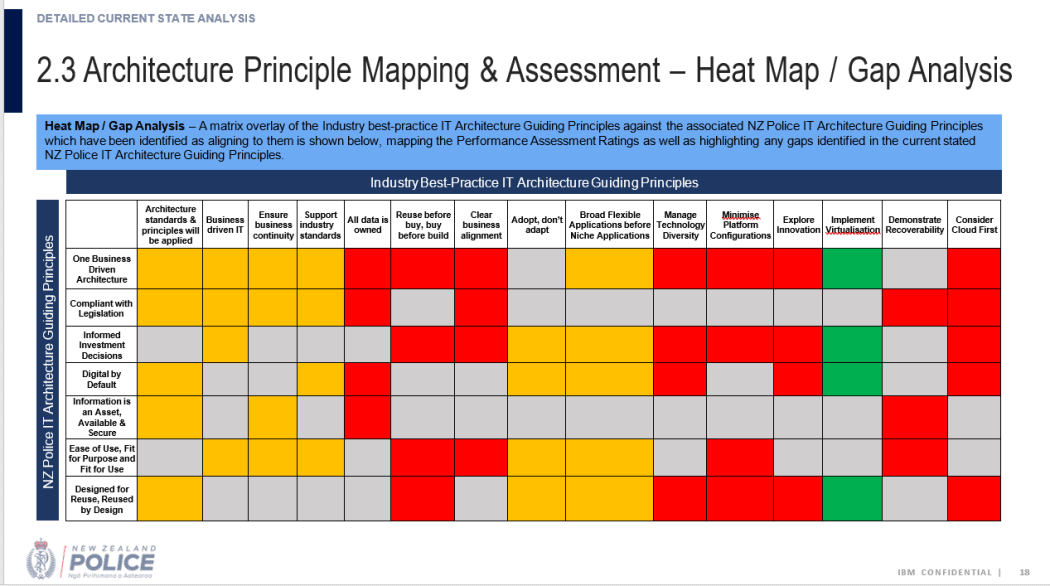
IBM’s 2021 evaluation of police ICT was stuffed with purple containers that raised purple flags.
Photo: Police OIA
IBM was now serving to to repair all this, through greater than $11 million in IT contracts it has with police.
The US tech large additionally discovered techniques had been duplicated, efficiency measures and priorities had been “ad hoc”, and an overarching enterprise structure was lacking.
There was little signal of correct strategising, which might get sticky politically, IBM warned: “Potential political fallout of not meeting ‘Cloud first’ all-of-government adoption if discovered by non-governing political parties,” it stated.
The police IT system was maybe distinctive in having monumental information swimming pools, the place it may be a life-and-death matter to have the ability to pay money for and analyse the information extremely quickly for frontline officers, as maybe, a taking pictures goes down.
However, until SearchX was constructed between March and September this 12 months, the principle information swimming pools had been siloed and didn’t share the likes of firearms and gang hyperlinks; the entire ICT system was referred to as “incomplete”, “disjointed”, “undefined”, “unclear” and “inconsistent” by IBM.
“Many business areas have their own ‘shadow IT’ for data management,” it stated.
“Data managed by ‘shadow IT’ is invisible to the rest of the organisation and is highly likely to fall outside of data recording standards.”
Police information boss Dr Dan Wildy instructed RNZ within the OIA the evaluation was about “surfacing how technology needed to be shaped to support future business initiatives and strategies”.
“It is not necessary nor sometimes possible for an organisation to target or achieve an optimised rating in each architectural domain,” Wildy stated.
“The purpose is typically to demonstrate a starting point to identify gaps in key areas and to work towards continuous improvement in these areas.”
Police state elsewhere it was “using technology to support our mission to prevent crime and harm through exceptional policing”.
The OIA paperwork present the ICT staff working properly in some respects, however at sixes and sevens in others, and underneath large strain.
“Projects [were] placed under pressure to deliver to timeframes they know they can’t meet.”
This strain led police early this 12 months to rule out shopping for a complete new intelligence search device – its paperwork point out choices such because the controversial Gotham by Palantir, Azure Cognitive Search and Siren – as a result of that will trigger ICT extra work. Instead, it expanded its IBM system and added new visible AI.
Another of the choices not pursued was Datawalk. The California firm promotes tech that finds connections from people to telephone numbers and name logs, automobiles, offences, “dealers”, firearms and addresses, amongst different issues.
It was not clear simply how far police have gotten with fixing all this.
ICT fixes by no means come low-cost, and within the New Zealand police’s case, many go hand-in-hand with large US tech companies which have had nice success increasing the regulation enforcement market at house and overseas.
So far, a collection of 5 upgrades, together with to “stabilise” the core National Intelligence Application, have price $31m – or 50 p.c greater than price range.
Police spending on contractors and consultants of every type, together with IT, virtually doubled to $91m final 12 months.
One spur was its spending on six main tasks together with the Tactical Response Model, that goals to make frontline officers safer, partly because of SearchX.
SearchX and a brand new visible analytics hyperlink the police databases for the primary time, and scoop up information from their OSINT group (open-internet searchers).
Police have refused to say what tech it makes use of to scrape the web – “providing such information to criminals would only harm the community”. One device is more likely to be from surveillance-for-hire firm Cobwebs, which like Cellebrite grew out of the hotbed of Israel’s intelligence neighborhood.
Around 2020, after police had launched an overhaul of its total intelligence system, a evaluate discovered it was so gappy and siloed that officers had just about given up on it.
“The intelligence function has lost relevance within some areas of police,” it stated, an OIA from 2021 showed.
Police needed to urgently improve it “to prevent a 9/11 moment”, it added.
This was compounded by the ICT flaws uncovered by IBM – the techniques weren’t working properly (information obtained “dirty” too simply, IBM stated, and police wasted money and time attempting to construct their very own options) and nor had been the intelligence instruments.
“It is necessary to look beyond our demand data, searching for additional context, nuance and information derived from the widest possible range of sources,” Wildy stated in 2021.
Among the highest priorities had been to get “predictive analytics” to “deliver precise and predictive targeting picture” of crime targets; and to get geospatial instruments for “time and space pattern analysis”.
Police obtained that new device this 12 months, ArcGIS, from US firm Esri that champions using mapping crime “hotspots”.
A police 2023 tech listing stated it didn’t produce hotspot maps, however in one other place it stated that it did.
Esri, addressing ethics, says, “GIS [Geographical Information System] is increasingly bound to and supplied by information from big data streams, artificial intelligence, and models that the GIS analyst did not create themselves”.
Big tech companies have discovered an enormous market with regulation enforcement globally for the likes of crime data-mining applied sciences and smart-maps, prompting pushback from the likes of the Tech Is Not Neutral marketing campaign.
Proponents argue data-driven policing can enhance public security; critics that it will possibly erode civil liberties.
A market analyst forecast the regulation enforcement software program market to develop by 50 p.c to about $50 billion in 5 years, with Asia-Pacific together with New Zealand providing “major opportunities … as the region has undergone significant political, social, and economic development over the past five years”.
Police had been approached for remark however stated it was not capable of come again to RNZ till presumably afterward Tuesday.
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link