
[ad_1]
Professor Pablo Fernandez Peñas (left), Associate Professor Ivan Kassal and Dr Tingrei Tan within the Sydney Nanoscience Hub. Photo: Stefanie Zingsheim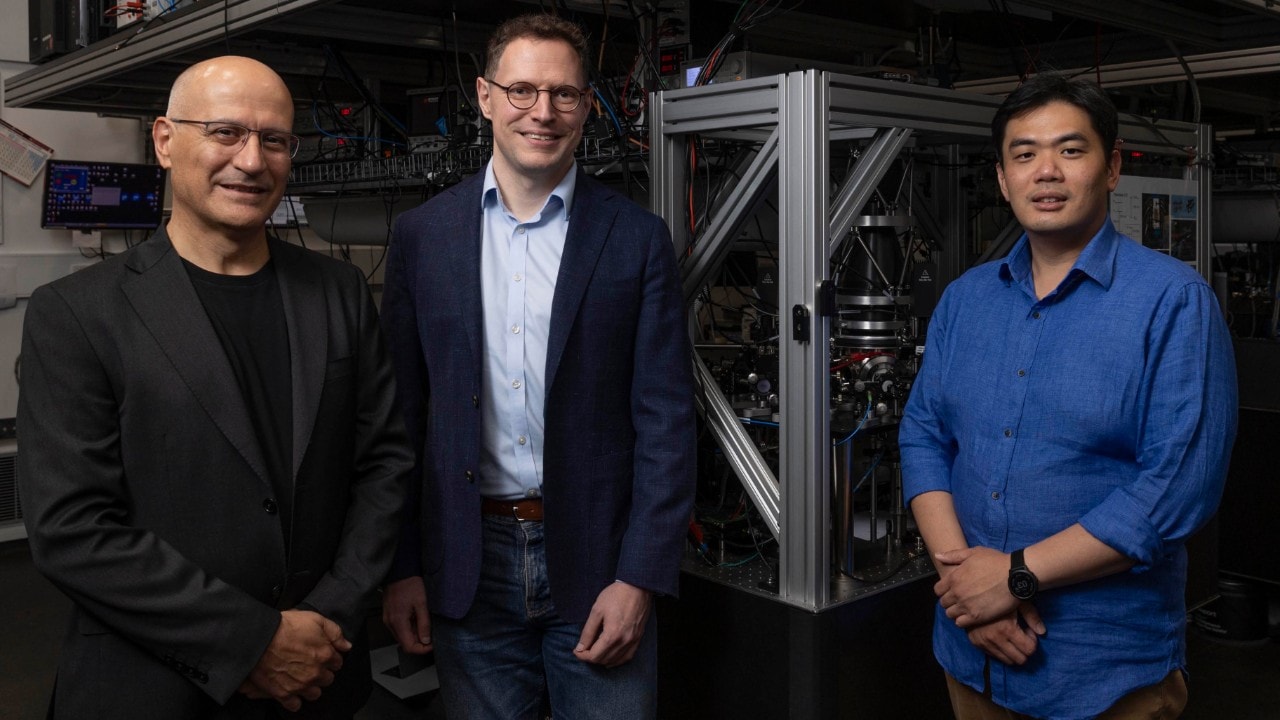
A workforce on the University of Sydney Nano Institute led by Dr Tingrei Tan has been awarded a contract by US-based non-profit organisation Wellcome Leap to develop helpful quantum know-how for software within the organic and well being sectors.
Quantum for Bio (This fallBio) is a multimillion-dollar program targeted on figuring out, growing and demonstrating functions in human well being that can profit from the quantum computer systems anticipated to emerge within the subsequent three to 5 years.
This fallBio has engaged a dozen groups globally with the University of Sydney the one Australian establishment awarded a contract.
The Sydney workforce is aiming to make use of quantum tech to develop new molecules that may deal with pores and skin cancers or enhance sunscreens.
Dr Tan stated: “We are excited to take part in Wellcome Leap’s daring imaginative and prescient of accelerating the functions of quantum computing in human well being functions.
“Our multidisciplinary research aims to address a critical bottleneck in today’s drug development – the inability of conventional computers to accurately predict quantum chemical dynamics in molecules.”
His workforce, primarily based within the Sydney Nanoscience Hub, will pioneer quantum options to deal with probably the most difficult issues in computational drug discovery. It will develop algorithms to simplify and allow correct quantum simulations that radically enhance our modelling of photoactive chemical reactions.
These reactions occur at speeds so quick they’re unable to be noticed in real-time. They are important to processes corresponding to photosynthesis and photo voltaic power, but additionally for sunscreens and photoactive medicines.
Analog quantum simulations permit scientists to gradual these processes down by an element of 100 billion occasions to take significant observations. The workforce recently published analysis in Nature Chemistry demonstrating for the primary time this outstanding slowdown in a quantum simulation.
The management of this multidisciplinary workforce consists of Dr Tan within the School of Physics, Associate Professor Ivan Kassal within the School of Chemistry, each within the Faculty of Science, and Professor Pablo Fernandez Peñas within the Sydney Medical School within the Faculty of Medicine and Health.
Associate Professor Kassal stated: “Understanding what occurs at a molecular degree when a cell absorbs mild, is a possible early software for quantum computer systems.
“Our joint research could unlock a whole new approach to understanding and treating disease, and to design new drugs. Our team will tackle these wicked problems by bringing together multidisciplinary expertise in quantum technology and chemistry together with medical researchers.”
Professor Fernandez Peñas, Head of Dermatology at Westmead Hospital in Sydney, stated: “Dermatology has a love/hate relationship with mild. Light is each the principle explanation for pores and skin most cancers – ultraviolet mild – but additionally a supply of power to deal with some types of pores and skin most cancers – purple mild in photodynamic remedy – and assist with different ailments, utilizing laser mild.
“A better understanding of how photo-reactions happen should allow us to design innovative molecules that will help to treat diseases or improve sunscreens.”
Dr Tan’s trapped-ion quantum pc within the Quantum Control Laboratory is on the experimental coronary heart of this analysis. The concept work is being constructed by Associate Professor Kassal’s workforce in Chemistry and the top software targets are being designed by Professor Fernandes Peñas’ workforce in Medicine.
Quantum know-how, nonetheless in its infancy, guarantees to revolutionise a variety of fields, together with cryptography, supplies science and drug design.
Director of Sydney Nano and a quantum theorist, Professor Stephen Bartlett, stated:
“The University of Sydney is one of the most suitable institutes in the world to conduct this research. The comprehensiveness of world-class research at the University provides an ideal platform to drive multidisciplinary problem solving to tackle some of the most challenging problems facing humanity.”
The Quantum for Bio program has three distinct phases spanning 2.5 years. Phase 1 contracts embody funding of as much as $US1.5 million ($A2.3 million) to develop quantum algorithms the place the quantum computing sources wanted (variety of qubits and program depth) ought to match throughout the goal sources outlined in this system announcement. If profitable, members will proceed to a second section involving large-scale simulations of the algorithms on high-performance classical computer systems.
Phase 3 will permit for the implementation of the algorithmic options on quantum {hardware}, attracting as much as $US2 million in additional funding.
The University of Sydney has one of many broadest and deepest quantum know-how packages globally, with world-class specialists in quantum concept, the event of quantum {hardware} and software program.
The University is a founding member of the Sydney Quantum Academy.
Since 2017 the University has been house to the Sydney Microsoft Quantum laboratory, led by Professor David Reilly.
Also in 2017, Professor Michael Biercuk used analysis developed on the University to launch Q-CTRL, Australia’s first venture-capital-backed quantum start-up.
[adinserter block=”4″]
[ad_2]
Source link